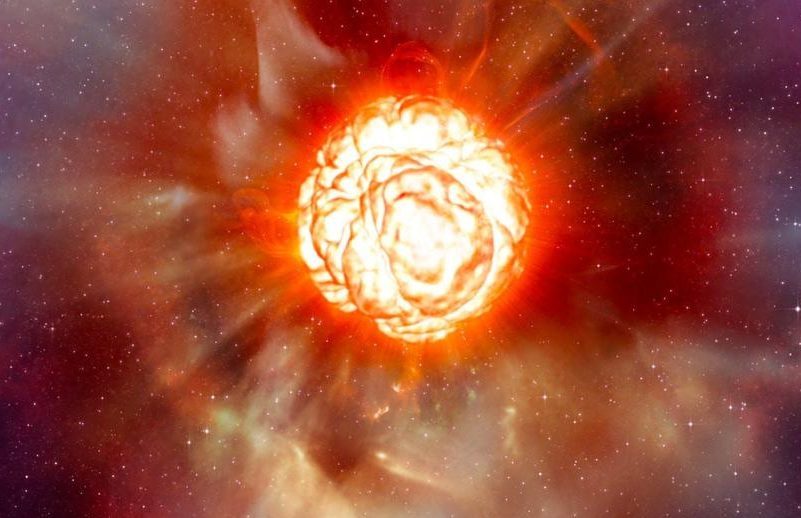

Will Betelgeuse explode soon?
On March 14, 2024, The American Association of Variable Star Observers (AAVSO) reported that the star Betelgeuse in the constellation Orion has dimmed by about 0.5 magnitude since late January. Betelgeuse is the nearest red supergiant star to Earth. It’s a variable star, so a change in its brightness isn’t unusual. But Betelgeuse is now dimmer than it’s been for several years. Is it possible we’re going to have another Great Dimming of Betelgeuse, such as the one in 2019-2020? If so, is it a sign of instability in this old red supergiant star? And could it mean Betelgeuse will explode soon?
Betelgeuse is the nearest potential supernova, but how far away is it? Distance estimates vary, but it’s probably within 1,000 light-years … a hop and a skip in galactic terms.
We know that someday, Betelgeuse will explode as a supernova. Then, it might become as bright as a full moon and possibly be visible in broad daylight!
But when will Betelgeuse explode?
When will it happen? The answer has been: Maybe today. Maybe a thousand years from now.
But since 2019, there’s been a noticeable uptick in Betelgeuse’s brightening and dimming. A paper published in June 2023 suggested not thousands of years but “tens of years” as the timescale for Betelgeuse’s going supernova.
The paper focused on the concept of stellar nucleosynthesis, the process that enables stars to shine. Inside stars, simple atoms fuse to make more complex atoms, with energy as a byproduct. It’s when a star’s nuclear fuel runs out that a supernova occurs. ArXiv.org, an open-access repository, published the new study on June 1, 2023, called The evolutionary stage of Betelgeuse inferred from its pulsation periods. The scientists said:
We conclude that Betelgeuse is … a good candidate for the next galactic supernova.
But let’s be clear. The history of supernovae observations within our own Milky Way is sketchy. Of course, we’d surely be lucky to see any galactic supernova, especially one as close as Betelgeuse, in our lifetimes.
The background buzz on Betelgeuse
Stars shine because they undergo thermonuclear fusion reactions in their interiors. Simply put, they fuse simple elements (like hydrogen) to create more complex elements (like helium), with energy as the byproduct. As massive stars (eight or more solar masses) age, they run out of the simplest fuels but progressively burn more complex fuels until, ultimately, their cores are made of iron and then nuclear burning ceases. At that point, with no more fusion taking place, the high temperatures in a star’s interior drop, and that means the high pressures in the star’s interior drop, too. The star collapses on itself, then rebounds in a terrific explosion: a supernova.
In this way, massive stars like Betelgeuse explode as Type II supernovae – collapsing rapidly and exploding violently – after they exhaust their fuel supply.
So, when a star explodes depends on what’s going on inside it, on how much fuel it has left, and on how close it is to collapse.
But what’s going on inside Betelgeuse?
A recent online study said:
We conclude that Betelgeuse is in the late stage of core carbon burning (…).
And the carbon-burning phase for a massive star like Betelgeuse lasts around 1,000 years. If we are “near the end” of that stage, then Betelgeuse has neared the end of its lifetime and may be about to explode, perhaps even in “tens of years.”
But are there other possibilities? Of course there are.
UniverseToday published a great story on Betelgeuse after the study above was released, that explains some of the science involved with drawing any conclusion about whether Betelgeuse will explode soon. The author pointed out that:
(…) What hasn’t attracted as much attention is the following part of the paper.
In fact, the researchers write, it is not possible to determine the exact evolutionary stage because surface conditions hardly change in the late stage close to carbon exhaustion and beyond. Astronomers can only see the surface, but what’s happening deep inside the star tells the tale.
The authors of the paper are really saying that, according to observations, data and modeling, Betelgeuse could explode sooner than thought. But — and this is critical — they don’t know what stage of core carbon-burning the star is in. Carbon burning could go on for a long time, according to some of the models that fit the data.
So, basically, we’re back to square one. Betelgeuse might explode tomorrow. It might explode in “tens of years.” Or it might explode in a thousand years.
But why did Betelgeuse dim in 2019?
Betelgeuse sparked excitement around the world when it began dimming noticeably late in 2019. Astronomers now refer to this event as the “Great Dimming of Betelgeuse”. As it was happening, many believed (and hoped!) the big event – the explosion of this relatively nearby star – was close at hand.
Of course – although Betelgeuse regained brightness, then dimmed again, brightened again, now dimmed again, and so on – it has not exploded yet.
So why did it dim?
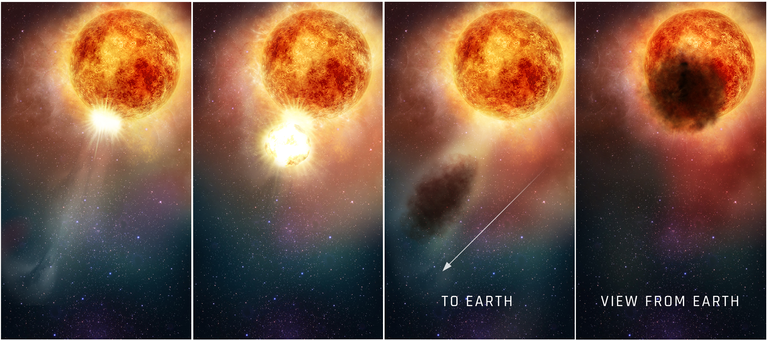
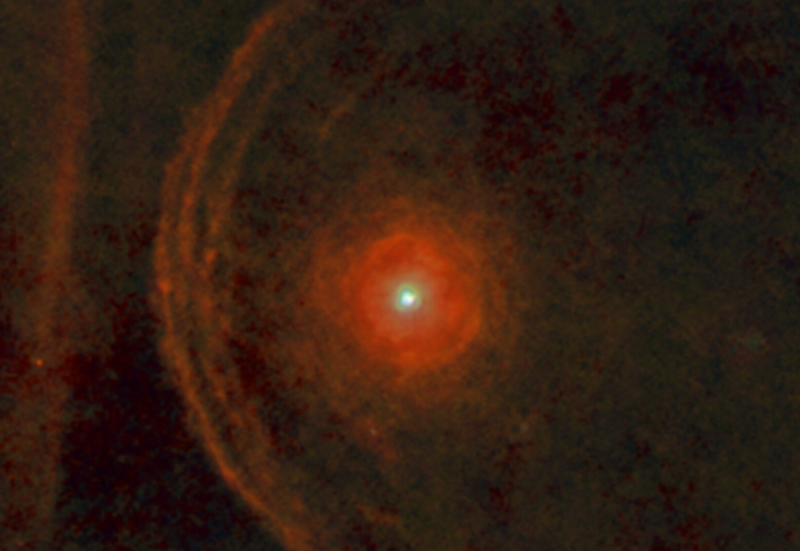
Analyzing data from NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope and several other observatories, astronomers concluded that the bright red supergiant star Betelgeuse quite literally blew its top in 2019. Betelgeuse lost a substantial part of its visible surface and produced a gigantic Surface Mass Ejection (SME). This is something never before seen in a normal star’s behavior.
Our sun routinely blows off parts of its tenuous outer atmosphere, the corona, in an event known as a coronal mass ejection (CME). But the Betelgeuse SME blasted off 400 billion times as much mass as a typical CME!
Read more: Betelgeuse is recovering from blowing its top
So, the Great Dimming of Betelgeuse in 2019 was apparently caused by a cloud of hot gas expelled by the star that temporarily blocked some of the star’s light.
Clearly, some game is afoot at Betelgeuse! And is it happening again?
Will its supernova destroy Earth?
Whenever Betelgeuse does blow up, our planet Earth is too far away for this explosion to harm, much less destroy, life on Earth. Studies indicate we’d have to be within 160 light-years of a supernova for it to harm us. And Betelgeuse is perhaps four times this distance.
Instead, anyone alive on Earth when Betelgeuse does finally explode will see an amazingly beautiful sight in the night sky – a very, very, very bright star.
And professional astronomers will be happy to have an exploded Betelgeuse so close. They’ll be able to study the star post-supernova.
Meanwhile, amateur astronomers and casual stargazers will enjoy the explosion, too. But the many who enjoy seeing Betelgeuse as Orion’s bright red star will dearly miss it when it’s gone!
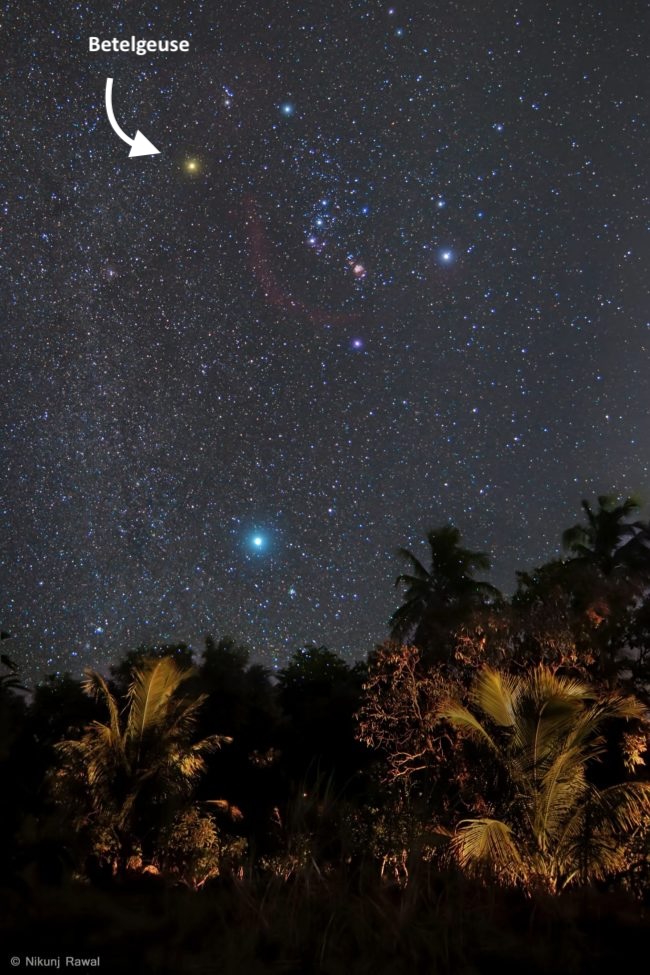
Betelgeuse in the night sky
At mid-northern latitudes, around the first of every year, Betelgeuse rises around sunset. The star is prominent on January and February evenings.
By the beginning of March, this star is due south in the early evening. By mid-May, it is briefly visible in the west after sunset. Betelgeuse travels behind the sun in early summer, and returns in the east before dawn by about mid-July. By early August, you can see Betelgeuse in Orion in the east before sunrise, where the constellation is known as the ghost of the summer dawn.
The star Betelgeuse has a distinctive muted orange-red color. It’s ideal for convincing non-believers that stars do, in fact, come in colors.
Stars designated as Alpha are typically brightest in their constellations. But Betelgeuse is Alpha Orionis, despite the fact that it’s fainter than Orion’s other bright star, Rigel.
Betelgeuse is the 10th-brightest star in the sky overall, and it’s the 7th-brightest star visible from most of the U.S., Canada, Europe and the majority of the Northern Hemisphere.

Pop culture, history and mythology
Remember the movie Beetlejuice? This star’s name is similar to that.
The proper names of many bright stars are Arabic in origin. This fact reflects the dominance of Arabic astronomers and astrologers during Europe’s Dark Ages. The name Betelgeuse is derived from an Arabic phrase that is usually translated as “The Armpit of the Giant.” Of course, the Giant refers to Orion, but – rather than an armpit – some authors see Betelgeuse as representing a hand or sometimes a shoulder. While it is not entirely clear what the name means, Betelgeuse marks the right shoulder of Orion in many old star maps.
In the ancient myths, Orion is most often associated with a giant, a warrior, a hunter, a god or some other anthropomorphic or animal figure, so it is not surprising that most depictions of Betelgeuse have an anatomical connection. The Sanskrit name signified an arm, too, for example, although it likely was really the leg of a stag. In parts of Brazil, Betelgeuse was seen as the hind leg of a caiman (crocodilian) or the foreleg of a turtle. On the other hand, in ancient Japan, Betelgeuse was considered to be part of the rim of a ceremonial drum. In Peru, it was one of four vultures about to devour a criminal.
The position of Betelgeuse is RA 05h 55m 10.3053s, dec +07° 24′ 25.4″.

Bottom line: Will Betelgeuse have another great dimming in 2024, and does this mean that the star will become a supernova soon? When it does explode, it’ll be bright enough from our earthly vantage point to shine during the day.











