In a separate story today, EarthSky reported on the possibility of stars made of dark matter. Scientists are calling them dark stars. And they’re different from ordinary stars, which are powered by fusion reactions deep in their interiors. Here’s how nuclear fusion works to power the sun and stars. This is an explainer from the U.S. Department of Energy. Edits by EarthSky.
How nuclear fusion works
An explainer from the U.S. Department of Energy. Edits by EarthSky.
Nuclear fusion reactions power the sun and other stars. In a fusion reaction, two light nuclei of atoms merge to form a single heavier nucleus. The leftover mass becomes energy.
Einstein’s equation (E=mc2) – which says in part that mass and energy can be converted into each other – explains why this process occurs.
If scientists develop a way to harness energy from fusion in machines on Earth, it could be an important method of energy production.
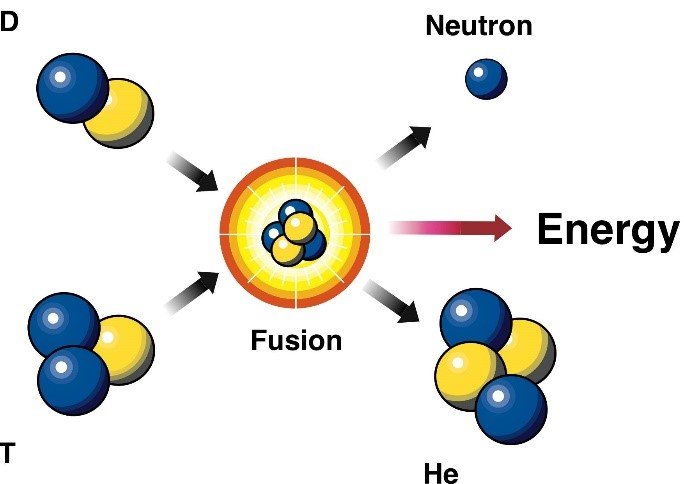
Fusion can involve many different elements in the periodic table. However, earthly researchers – who are working on fusion energy applications – are especially interested in the deuterium-tritium (DT) fusion reaction. DT fusion produces a neutron and a helium nucleus. In the process, it also releases much more energy than most fusion reactions.
In a potential future fusion power plant such as a tokamak or stellarator, neutrons from DT reactions would generate power for our use. Researchers focus on DT reactions both because they produce large amounts of energy and they occur at lower temperatures than other elements.
Bottom line: Nuclear fusion powers our sun, and is the energy source of all the stars in our night sky. Here’s how nuclear fusion works to make stars shine.











