The celestial ocean in the autumn sky
Look for what Northern Hemisphere stargazers call the celestial ocean in the autumn sky. And it’s overhead in the spring sky for Southern Hemisphere stargazers. The September equinox took place on September 23 at 1:04 UTC. So now we’re well into these seasons, both on the Earth below and in the sky.
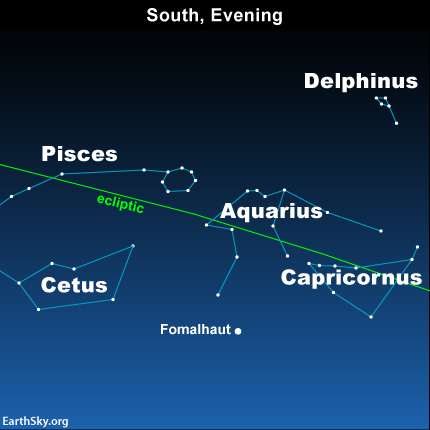
The chart at the top of this post makes this part of the sky look crowded. But, if you look at the sky, there is only one bright star shining here. However, in 2022, the bright planets Saturn and Jupiter are joining the celestial ocean. The stars making up the celestial ocean are not very bright. So, you’ll only see these dim stars, if you’re looking in a dark-enough sky. Still, their constellations are identifiable, and no doubt the ancients knew them well. You can come to know them well, too.
Note for Southern Hemisphere stargazers: You can see this region of the sky, too. In fact, you can see them better than we can in the north because, for you, these planets and stars are higher in the sky, closer to overhead.
Try Stellarium for a specific view from your location.
What can you see in celestial ocean of the sky?
Let’s start with the brightest objects visible in and around this region. In 2022, the bright planets visible across this stretch of evening sky (looking west to east) are Jupiter and Saturn. A single bright star – shown on the chart above – is noticeable, but not as much this year because the planets outshine it. Still, you’ll want to identify Fomalhaut, brightest star in the constellation Piscis Austrinus the Southern Fish.
Other constellations in the celestial sea (looking west to east) include Capricornus the Sea Goat, Delphinus the Dolphin, Aquarius the Water Carrier, Pisces the Fish, Cetus the Whale and Eridanus the River. And Fomalhaut is located in the constellation Piscis Austrinus the Southern Fish: another swimmer in the celestial ocean.

No matter where you are on Earth, you need a very dark sky, a couple of hours after sunset, to see the constellations of the heavenly sea. Many of the constellations in this part of the sky are connected with water. Maybe because the sun was moving in front of these stars on the great pathway of the ecliptic during a rainy season long ago.
Capricornus the Sea Goat.
Capricornus represents a Sea Goat, but has the shape of an arrowhead on our sky’s dome. By late October and early November, in early evening, you’ll find this constellation past the meridian, or line drawn on the sky’s dome from due north to due south. Read more about Capricornus.
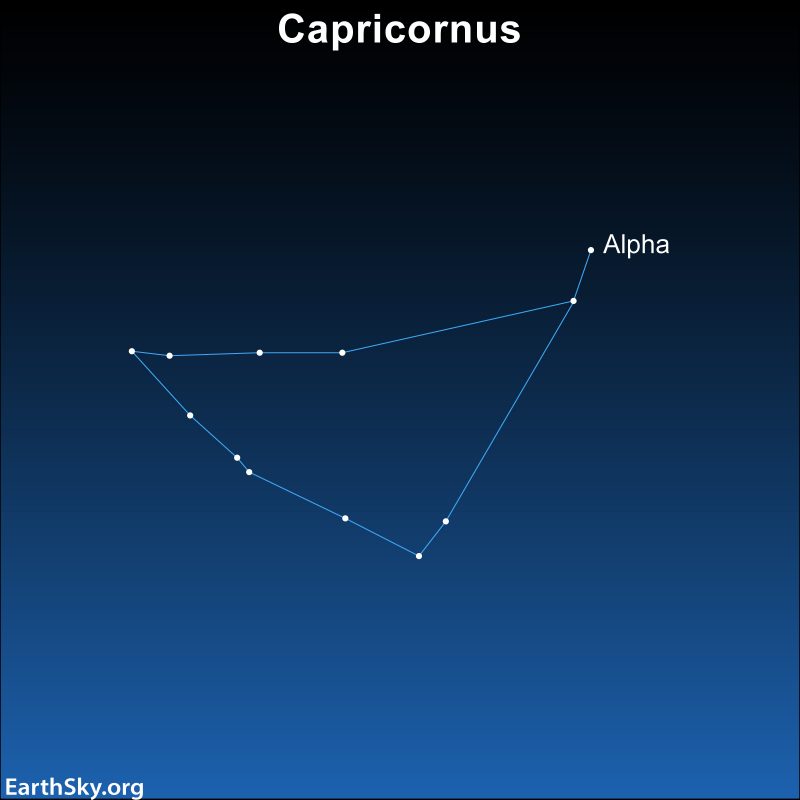
Delphinus the Dolphin
Delphinus is a truly delightful little constellation that really resembles a dolphin leaping among the waves. And Delphinus is one of the earliest constellations, first cataloged by the Greek astronomer Ptolemy in the second century.
Some myths say Delphinus is the Dolphin that carried a Greek poet – Arion – safely away from his enemies. Others say this sky Dolphin represented the dolphin sent by the sea god Poseidon to find Amphitrite, the Nereid he wanted to marry. Read more about Delphinus and other small constellations.
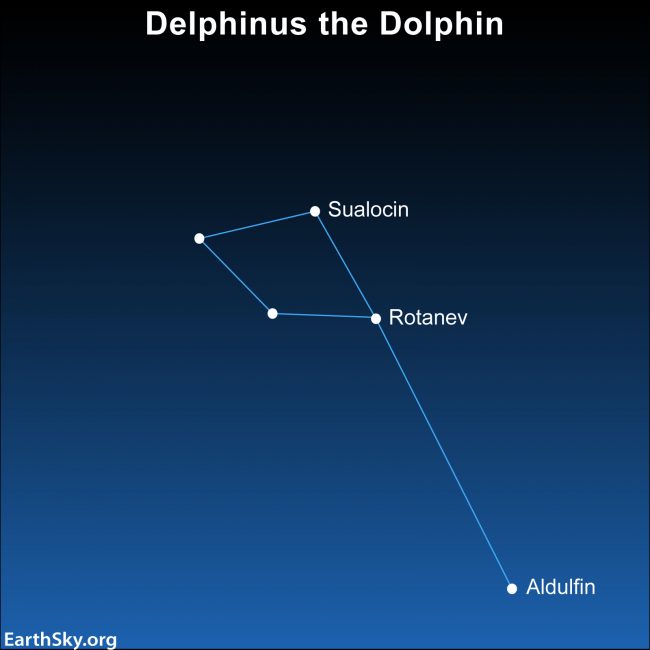
Fomalhaut and Piscis Austrinus.
In nearly every northern autumn, because the stars around it are so faint, the star Fomalhaut appears to shine in solitary splendor. But not this autumn, because two bright planets are visible in this part of the sky. Still, Fomalhaut is easy to spot. It shines brightly all alone in a large dark patch of sky.
Fomalhaut is sometimes called The Lonely One or The Solitary One. It’s said to be lonely because it’s noticeable as the only bright object in an otherwise “empty” region of the sky (no region of the sky is truly empty, of course). Fomalhaut is a blue-white star, located only a couple of dozen light-years away. Read more about Fomalhaut here.
Meanwhile, Piscis Austrinus is a small, round pattern of stars, supposedly the open mouth of the Southern Fish. But don’t expect to see a fish in these stars, when you find Piscis Austrinus in a dark sky. Look for it below a zig-zag line of stars stemming from Aquarius the Water Carrier. In skylore, the Water Carrier is supposed to be pouring water into the open mouth of Piscis Austrinus.
Aquarius the Water Carrier
Aquarius is usually portrayed as a man pouring a stream of water into the mouth of the Southern Fish. Which is interesting since fish don’t drink water. If your sky is dark, you can see an asterism – or noticeable pattern of stars — left of the star Sadal Melik. This pattern, shown in the orange dashed oval in the star map below, is called the Water Jar in Aquarius. Imagine a cascade of faint stars as water, making a zigzag stream of stars, flowing down toward the star Fomalhaut. Read more about Aquarius the Water Carrier.
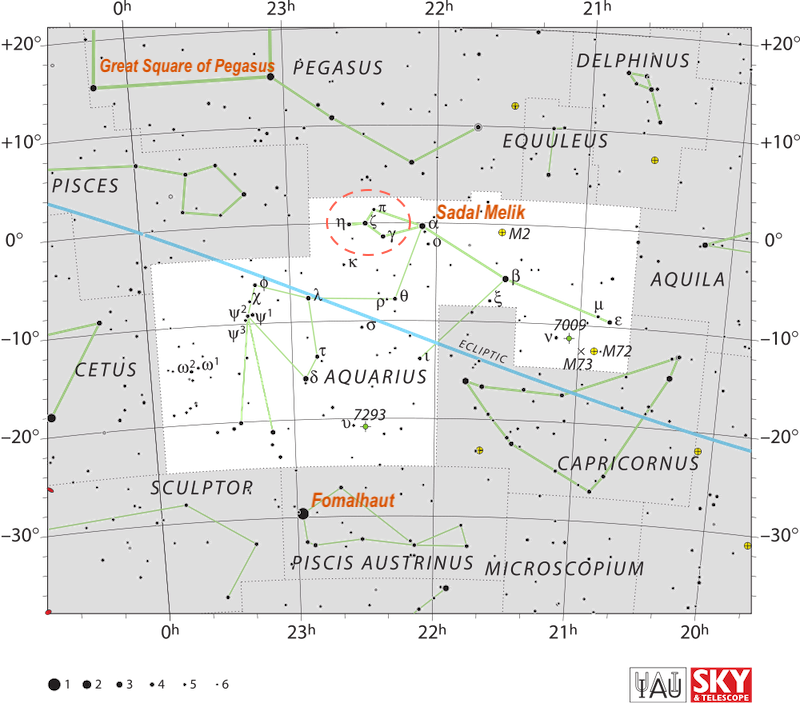
Pisces the Fishes
As seen from across the globe, Pisces reaches its high point for the night at about 10 p.m. local standard time in early November. Pisces the Fishes is sometimes called the first constellation of the zodiac because the sun appears in front of this constellation at the time of the March equinox.
The constellation has the shape of a graceful V on our sky’s dome. Pisces’ alpha star Al Risha can be found where the two tails of the Fishes come together, at the point of the V. In October and November 2022, you’ll also find the bright planet Jupiter in Pisces. Read more about Pisces the Fishes.
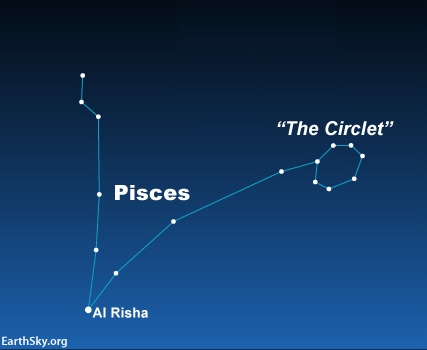
Cetus the Whale
Cetus is a somewhat unremarkable constellation. We call it a Whale, but it was a sea-monster in Greek mythology. It has one irresistible feature, though, its star Mira the Wonderful. Mira isn’t the brightest star in Cetus, but it’s the best known of the Whale’s stars. Mira isn’t visible to the unaided eye much of the time. Because Mira varies in brightness, ranging from visibility as a rather faint star to total invisibility to the eye alone. Mira’s last brightness maximum was in July 2022, and is no longer visible to the eye now. Read more about Mira and Cetus.
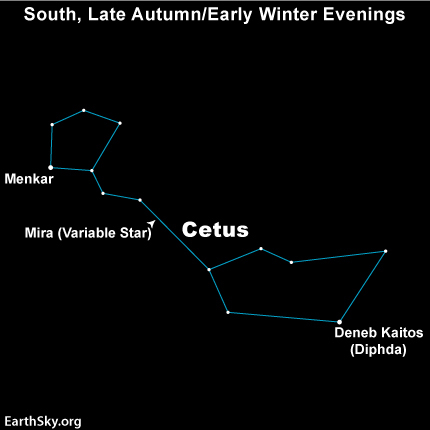
Eridanus the River wraps up the celestial ocean
The great river of the sky, Eridanus, rises later at night than the other “watery” constellations in autumn, but, once it’s up, is large and easy to see in a dark-enough sky. That’s because the northern part of this constellation is located near the extremely prominent constellation Orion the Hunter. Eridanus appears to swell up in a great loop near Orion, then meander southward, Then finally – for most in the Northern Hemisphere – dropping out of sight below the southern horizon before it reaches its end.
But if you are far enough south – below 33 degrees north latitude – you’ll spot the bright star Achernar, the End of the River. Read more about Achernar and Eridanus.
Bottom line: The region of the sky around Fomalhaut contains what the ancients saw as the “watery” constellations or a celestial ocean.
EarthSky’s guide to the visible planets and night sky
EarthSky astronomy kits are perfect for beginners. Order yours from the EarthSky store.











