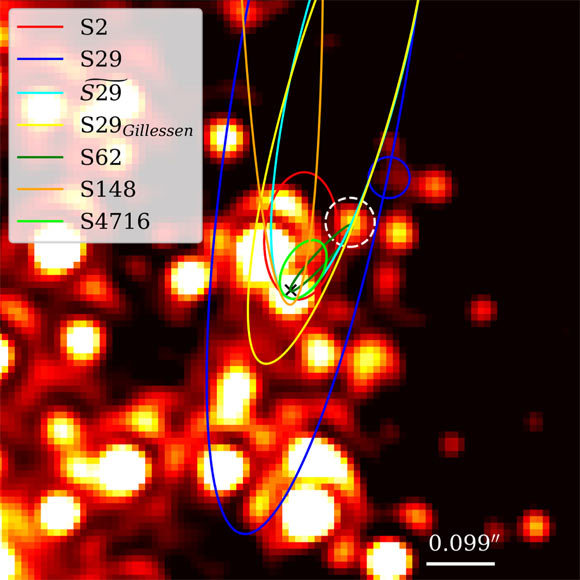
Speedy star orbits Milky Way black hole
Scientists in Europe said on July 5, 2022 that they’ve discovered the fastest-known star orbiting a black hole. And not just any black hole … it’s orbiting Sagittarius A*, the giant black hole at the center of our own Milky Way galaxy. Our central black hole weighs in at some 4 million times our sun’s mass. The new-found star is called S4716. It reaches speeds in orbit of 5,000 miles per second (8,000 kps) around the black hole, or about 5,000 times faster than the fastest fighter jet.
Imagine seeing a star – a huge, self-luminous ball of roiling gases – streaking past at this speed! By the way, by contrast, our Earth moves at 18 miles per second (about 30 kps) around our sun.
The scientists who made the discovery are at the University of Cologne and Masaryk University in Brno (Czech Republic). Their work is published in the peer-reviewed Astrophysical Journal.
Our Earth takes a year to orbit our sun once. And S4716 takes four years to go once around the black hole. Consider that Earth is one astronomical unit from the sun: that’s about 90 million miles (about 150 million km). S4716 is some 100 times the Earth-sun distance to the black hole (100 astronomical units). That’s a small distance by astronomical standards.
A statement from these scientists explained:
In the vicinity of the black hole at the center of our galaxy is a densely packed cluster of stars. This cluster, called S cluster, is home to well over a hundred stars that differ in their brightness and mass. S stars move particularly fast…
Florian Peisker of Masaryk University led the study and explained:
One prominent member, S2, behaves like a large person sitting in front of you in a movie theatre: it blocks your view of what’s important. The view into the center of our galaxy is therefore often obscured by S2. But, in brief moments, we can observe the surroundings of the central black hole.
These scientists used a total of five telescopes to observe the star, with four of the five combined into a single large telescope, “to allow even more accurate and detailed observations,” these scientists said. They said their discovery sheds new light on the origin and evolution of the orbit of fast-moving stars in the heart of the Milky Way.
Michael Zajaek of Masaryk University in Brno was also involved in the study. He said:
‘The short-period, compact orbit of S4716 is quite puzzling. Stars cannot form so easily near the black hole. S4716 had to move inwards, for example by approaching other stars and objects in the S cluster, which caused its orbit to shrink significantly.’
Peissker added:
For a star to be in a stable orbit so close and fast in the vicinity of a supermassive black hole was completely unexpected and marks the limit that can be observed with traditional telescopes.
Bottom line: Newly discovered speedy star S4716 is the fastest-known star orbiting our Milky Way’s central black hole.
Source: Observation of S4716: A star with a 4-year orbit around Sgr A*











