NASA engineers at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in Pasadena, California, will be among the most avid watchers of the launch of the Insight Mars mission on Saturday, May 5. That’s because InSight’s rocket will also carry the world’s first pair of deep-space CubeSats. As the video above explains, the CubeSats – whose mission is called Mars Cube One, or MarCO – are briefcase-sized mini-satellites. If all goes well, the NASA engineers who developed them hope they’ll provide a demonstration of a new miniaturized deep-space communications technology that should be much faster than existing technologies. The engineers said this new technology could:
… change the way deep-space spacecraft phone home.
The MarCos even have nicknames. NASA engineers call them Wall-E and Eva, for Pixar characters. The MarCOs won’t produce any science of their own. They’re not needed to make InSight a success; the lander will rely on NASA’s Mars orbiters to send back its data.
But the CubeSats – first developed to teach university students about satellites – are exciting stuff. Andy Klesh, MarCO’s chief engineer at JPL, explained MarCO’s purpose on the InSight mission this way:
These are our scouts. CubeSats haven’t had to survive the intense radiation of a trip to deep space before, or use propulsion to point their way towards Mars. We hope to blaze that trail.

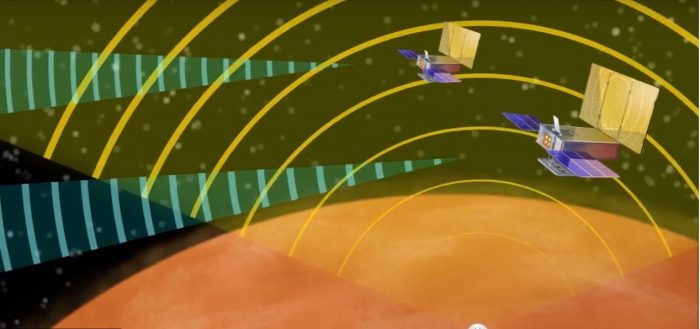
NASA said the MarCOs are intended to journey with InSight on its cruise through space; if they survive the trip, each is equipped with a folding high-gain antenna to relay data about InSight as it enters the Martian atmosphere and lands. NASA explained:
Survival is far from guaranteed. As the saying goes: space is hard. The first challenge will be switching on. The MarCO batteries were last checked in March by Tyvak Nano-Satellite Systems of Irvine, California, which inserted each CubeSat into a special dispenser that will propel it into space. Those batteries will be used to deploy each CubeSat’s solar arrays, with the hope that enough power will be left over to turn on their radios. If power is too low, the MarCO team may hear silence until each spacecraft is more fully charged.
If both MarCOs make the journey, they’ll test a method of communications relay that could act as a “black box” for future Mars landings, helping engineers understand the difficult process of getting spacecraft to safely touch down on the red planet.
That’s important because, as you know if you follow space history, Mars landings are notoriously difficult.

NASA appears to be all in for the CubeSat idea. It explained:
NASA scientists are eager to explore the solar system using CubeSats. JPL even has its own CubeSat clean room, where several flight projects have been built, including the MarCOs. For young engineers, the thrill is building something that could potentially reach Mars in just a matter of years rather than a decade.
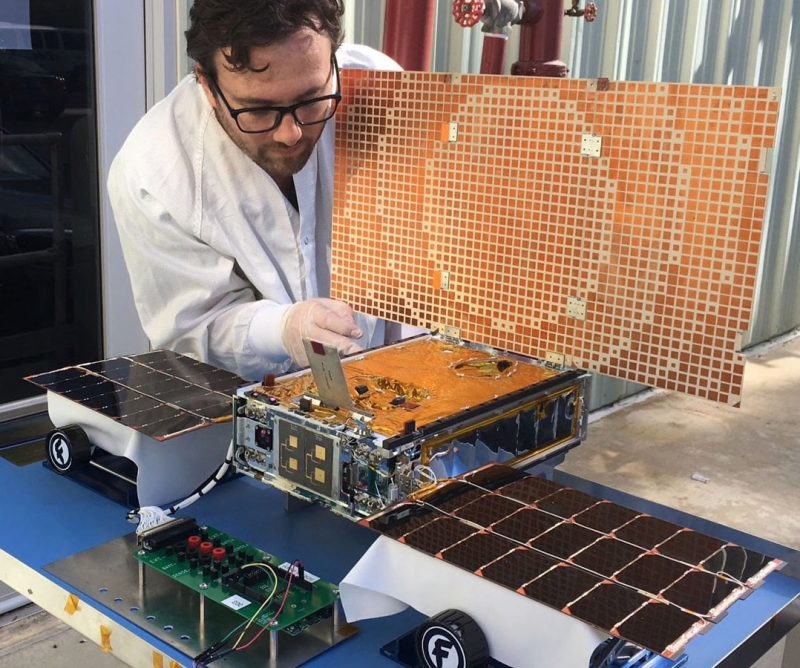

Klesh added:
We’re a small team, so everyone gets experience working on multiple parts of the spacecraft. You learn everything about building, testing and flying along the way. We’re inventing every day at this point.
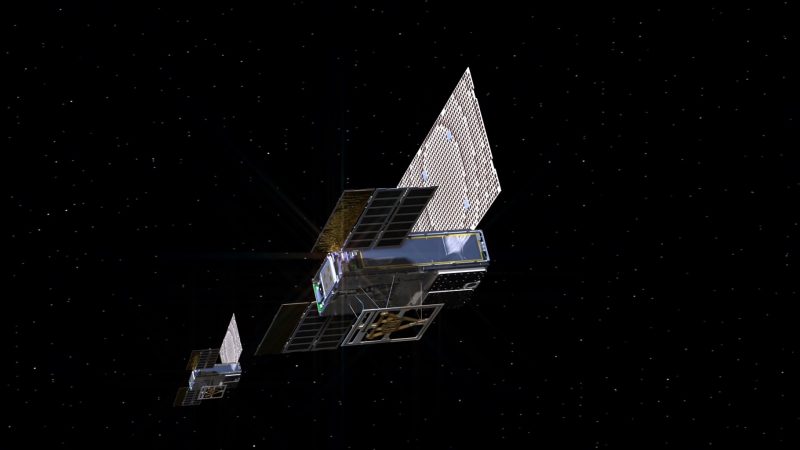

Bottom line: The 2 briefcase-sized CubeSats – collectively known as MarCO, and nicknamed Wall-E and Eva – are designed to demonstrate much-faster communications between Earth and Mars. If they survive the trip, and work as expected, the communications could happen in nearly real-time (allowing some minutes for light travel time).











