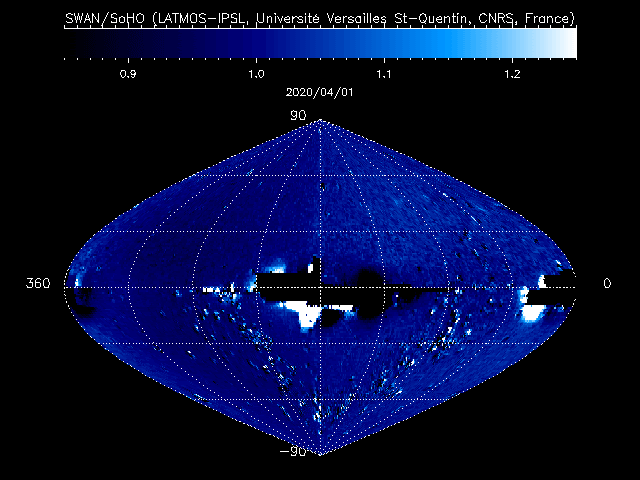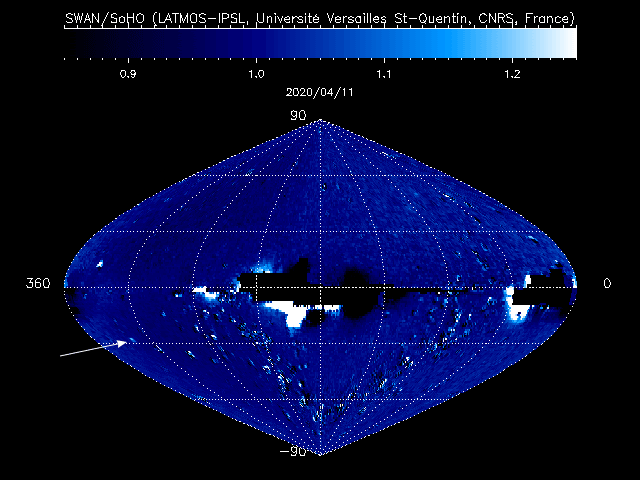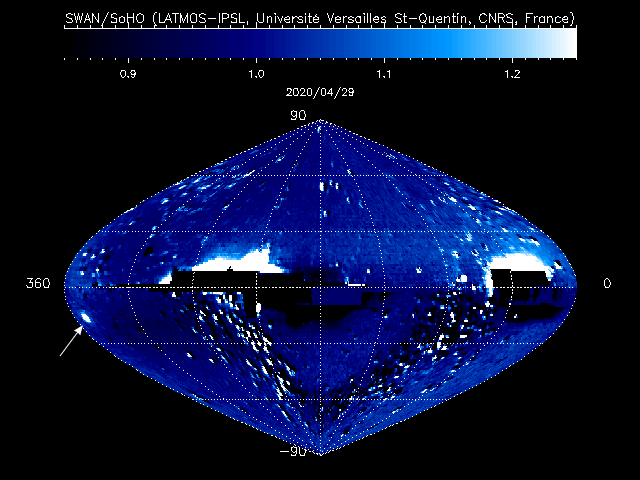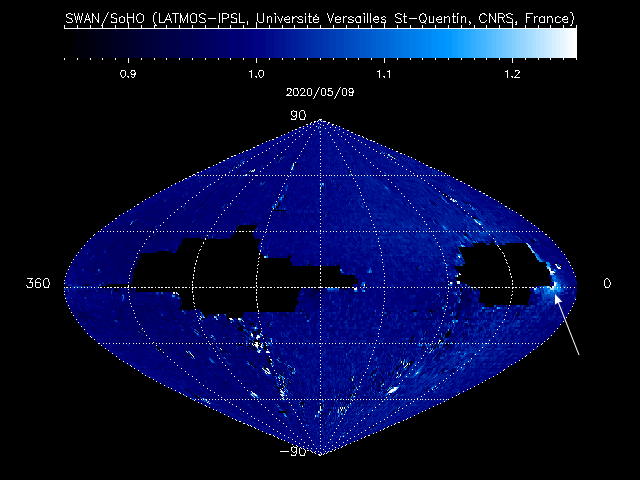
Currently crossing the skies above Earth, comet C/2020 F8 (SWAN) is grazing the northeastern horizon before dawn now and has some potential to become a more prominent object by late May or early June. Yet it wasn’t discovered by someone looking up at the night sky. Instead, the person was looking at a computer screen.
Amateur astronomer Michael Mattiazzo from Australia spotted this icy visitor from the outer solar system while inspecting images that had been posted online from the Solar Wind ANisotropies (SWAN) instrument aboard SOHO, the ESA/NASA Solar and Heliospheric Observatory.
SWAN captures images in ultraviolet light, including a specific ultraviolet wavelength called Lyman alpha. This is a wavelength that is characteristically emitted by hydrogen atoms. The instrument’s primary goal is to map changes in the solar wind, the variable flow of charged particles that is continuously released by the sun into interplanetary space. In addition, it has become an effective discoverer of comets, too, because comets are also sources of hydrogen.
Read more and find charts: Will you see Comet SWAN?
Check out the raw SOHO/SWAN images online
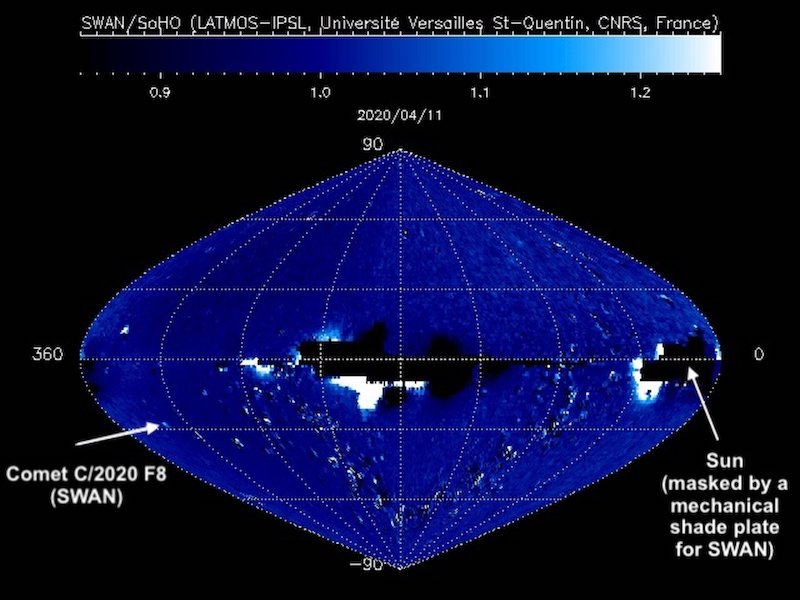
In the case of a comet, the hydrogen comes from the water vapor the icy core releases into space when heated by the sun. And there is more, as solar radiation can break water molecules (H2O) into a single hydrogen atom (H) and a hydrogen-oxygen pair (which scientists call a hydroxyl radical, or OH). The result is a cloud of hydrogen that surrounds the comet, giving off a bright spot of Lyman-alpha light that can be spotted in the SWAN maps.
Almost every day, SWAN records a complete map of the sky. These raw sky maps are full of stars, making it difficult to pick out new comets, which may arrive at random from any direction. To make the job easier, successive maps are automatically subtracted from one another, removing the stars and leaving only variable or moving sources visible.
These “difference images” are regularly posted online on the SOHO website, meaning that anyone with internet access can look at these “comet tracker’s maps” and join the search for new comets. To date, 12 of them have been spotted in the SWAN data since 1996, all of them by amateur astronomers, or citizen scientists as they are also known.
In the case of this current comet, Mattiazzo (who has already discovered eight comets using this method) found it by comparing the SWAN maps from several days in early April 2020.
From discovery to observation
Once the comet had been announced, Austrian astrophotographer Gerald Rhemann obtained a beautiful image of it from the desert in Namibia, clearly showing the spherical gas cloud of the comet’s coma and its extended ion tail. When the image was published as Astronomy Picture of the Day (APOD) on April 29, it helped bring the comet to wide scale attention.
Another image, taken a few days later by British astrophotographer Damian Peach using a remote telescope in Chile and also featured as APOD, portrays the impressive comet’s tail as it closed in on Earth. The closest approach was about May 13, at around 85 million km (53 million miles) from our planet.
The SWAN team’s comet expert, Michael Combi from the University of Michigan, estimates that by April 15 the comet was ejecting about 1300 kg (2,900 lbs) of water vapor every second, or about 4.4 x 1028 H2O molecules every second. That is a fast rate of ejection when compared to other comets. Jean-Loup Bertaux, former principal investigator and proposer of the SWAN instrument, said:
This is already three times more than Comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko at its best, when it was visited by ESA’s Rosetta mission between 2014 and 2016.
Will comet SWAN become an obvious naked eye object?
The comet’s vigor could be significant for observers on Earth. The more material ejected from the comet, the more sunlight it reflects and the more visible it becomes. The comet has moved from the southern to the northern skies. It has not brightened as expected, based on estimates from last month. However, it could brighten as it approaches its May 27 perihelion, or closest point to the sun – if it survives that long.
Comets are fragile objects, and can often break apart as they approach the sun. In late April, the much anticipated comet ATLAS suffered this fate, breaking into at least 30 fragments. Comet SWAN is now entering the “danger zone” and – at its closest point to the sun on May 27 – the solar heating will be at its maximum.
It can be extremely difficult to predict the behavior of comets that make such close approaches to the sun, but scientists are hopeful that comet SWAN will remain bright enough to see as it continues its journey. If the comet survives, stargazers on Earth should look for it near the bright star Capella in the constellation of Auriga the Charioteer. This is almost certainly the only time the comet will be visible in our lifetimes: estimates are not yet fully precise, but it is clear that the comet’s orbital period is measured in thousands or even millions of years.
Find charts and observing tips for comet SWAN here.
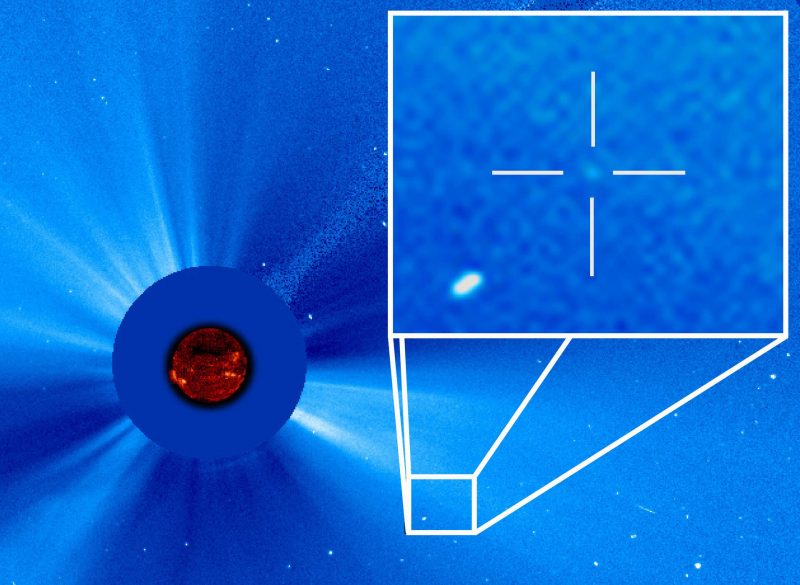
Waiting for the 4,000th comet
Although comet SWAN is only the 12th discovery from that particular instrument, it is the 3,932nd comet discovered by SOHO.
This extraordinary number is thanks to the Large Angle and Spectrometric Coronagraph Experiment (LASCO) instrument, with significant help from members of the public.
Karl Battams is LASCO team comet expert at the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory and lead researcher of the Sungrazer Project. He said:
Almost all of SOHO’s comet discoveries so far have been made by citizen scientists scouring images returned by SOHO’s LASCO instrument.
Bernhard Fleck, ESA SOHO project scientist, said:
It’s extremely exciting that our sun-watching observatory has spotted so many comets since its launch in 1995. We are eagerly awaiting, along with comet enthusiasts around the world, for the 4,000th discovery, which might happen real soon.
Bottom line: Currently crossing the skies above Earth, comet C/2020 F8 (SWAN) is grazing the northeastern horizon before dawn now and has some potential to become a more prominent object by late May or early June. Yet it wasn’t discovered by someone looking up at the night sky. Instead, the person was looking at a computer screen.











