Noctilucent cloud season is here! And we’re hearing that it’s shaping up to be the best season in years. Europe has had excellent, vivid views of these night-shining clouds in the second half of June. Check out the photos below from the EarthSky community!
Why such a strong showing of these clouds that shine after sunset in 2024? It might be a couple of things. According to Spaceweather.com, one factor could be the many recent SpaceX launches. June saw seven Starlink launches, plus the GOES-U launch with a Falcon Heavy rocket on June 26. New Scientist also pointed out that a record amount of water vapor from the Tonga volcano’s 2022 eruption is still in Earth’s atmosphere. And Spaceweather.com said:
Yes, that was two years ago, but it takes about two years for the vapor to circulate up to the mesosphere where noctilucent clouds form.
Noctilucent clouds in 2024
Do you have images of the 2024 noctilucent clouds to share? We’d love to see them! Submit them to EarthSky Community Photos.
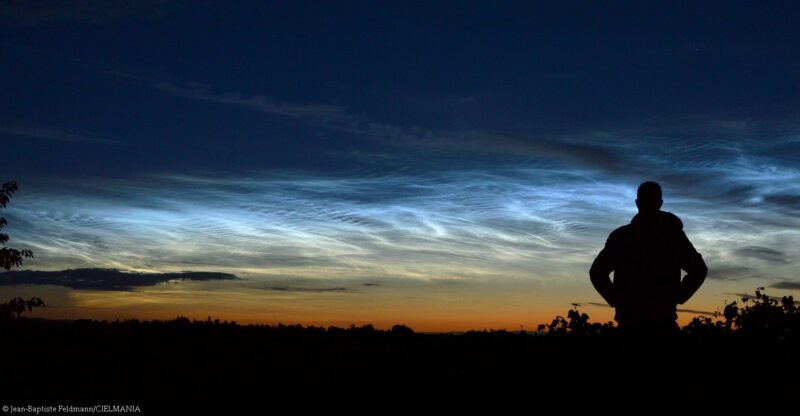
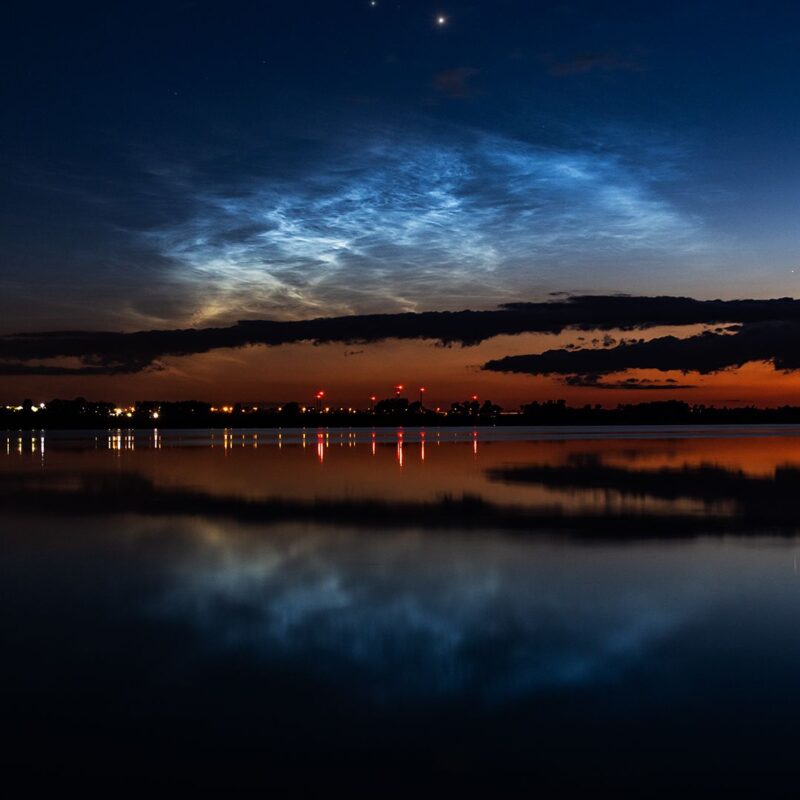
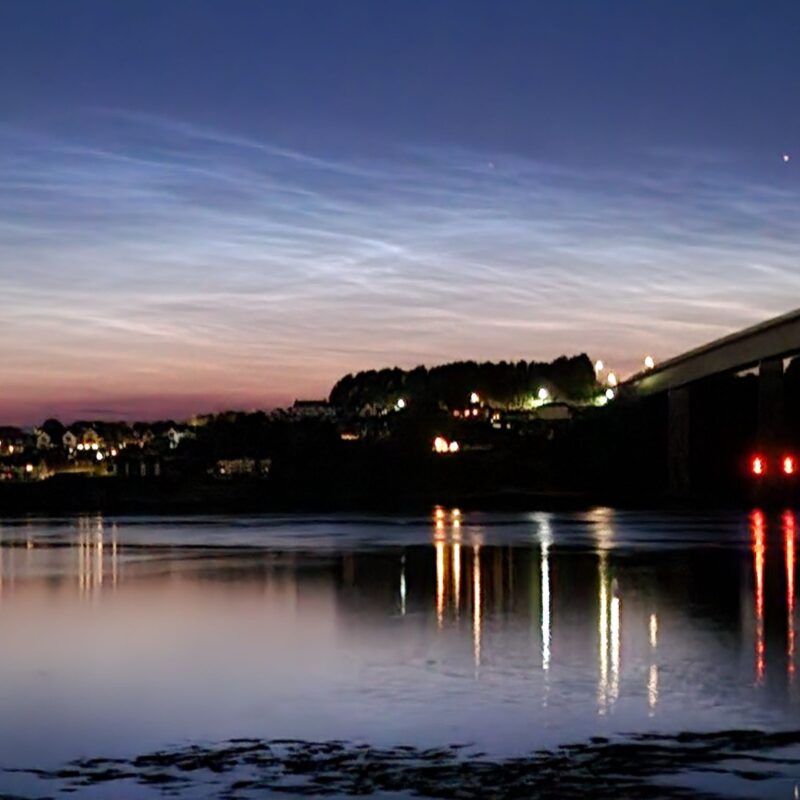
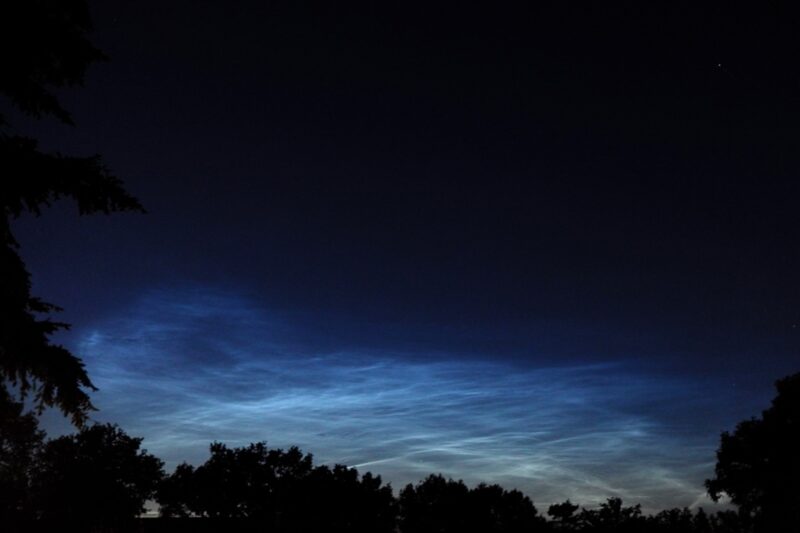
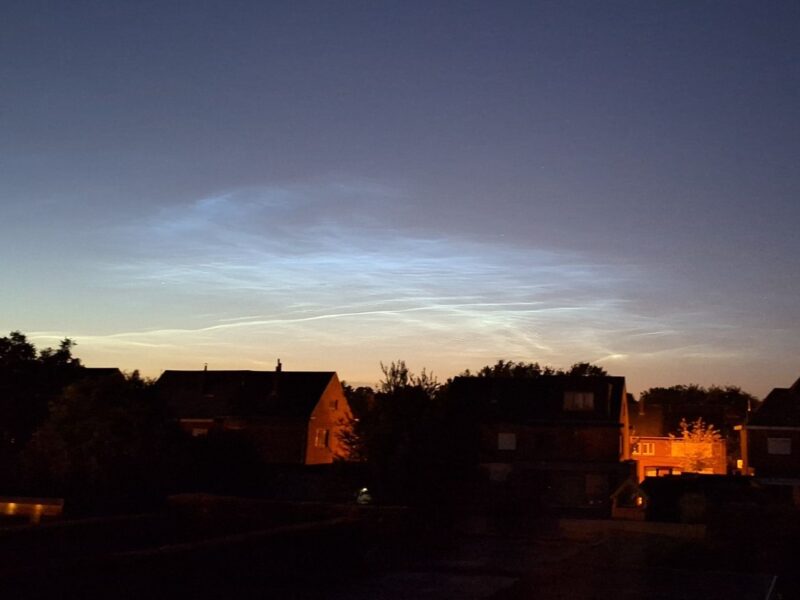





Noctilucent Clouds seen from Kendal, Cumbria, at 01:35 on July 1st 2024… One of the best displays I've seen… pic.twitter.com/eGRIPFcebV
— Stuart Atkinson (@mars_stu) July 1, 2024
What are noctilucent clouds?
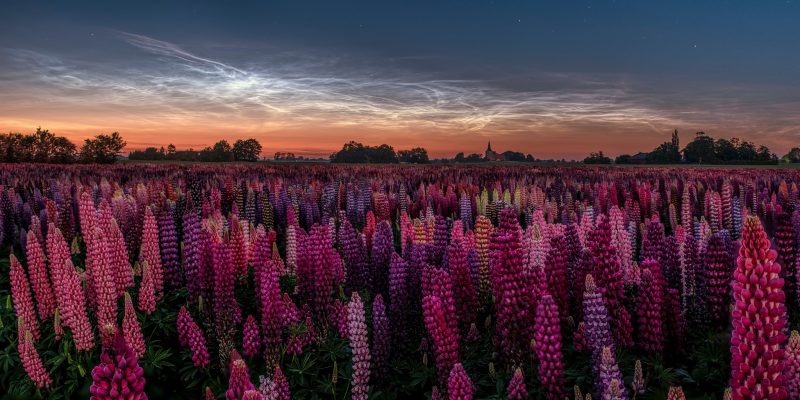
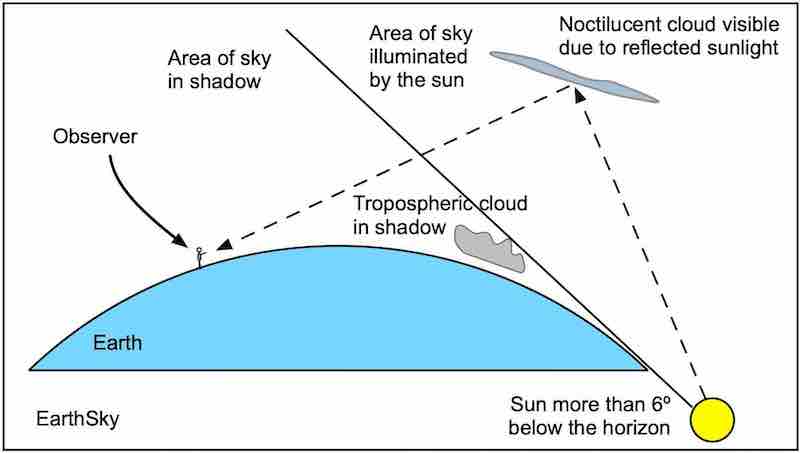
Noctilucent clouds, or night-shining clouds, are thin clouds high up in Earth’s atmosphere – the mesosphere – as much as 50 miles (80 km) above Earth’s surface. Scientists think they’re made of ice crystals that form on fine dust particles from meteors. They can only form when temperatures are incredibly low and when there’s water available to form ice crystals.
So, why do these clouds – which require such cold temperatures – form in the summer? It’s because of the dynamics of the atmosphere. In fact, you actually get the coldest temperatures of the year near the poles in summer at that height in the mesosphere.

Rising air
Here’s how it works: during summer, air close to the ground heats up and rises. Since atmospheric pressure decreases with altitude, the rising air expands. But, when the air expands, it also cools down. This, along with other processes in the upper atmosphere, drives the air even higher causing it to cool even more. As a result, temperatures in the mesosphere can plunge to as low as -210 degrees Fahrenheit (-134 C).
In the Northern Hemisphere, the mesosphere reaches these temperatures by mid-May in most years.
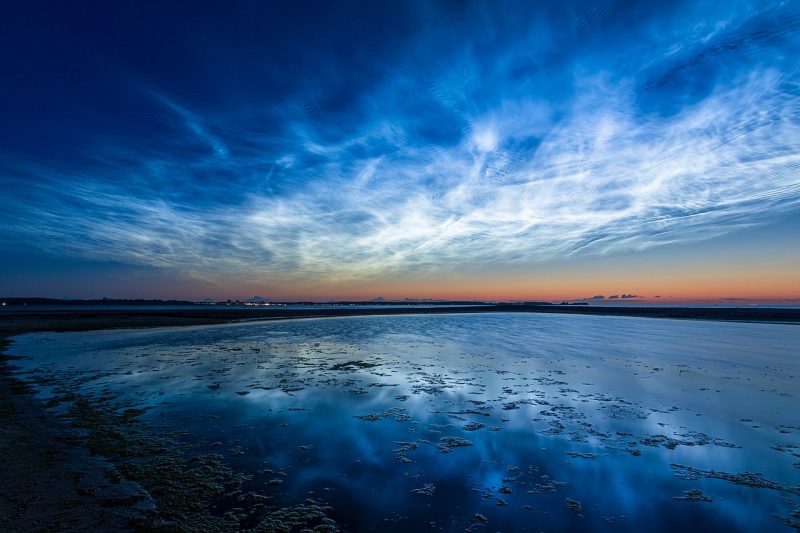
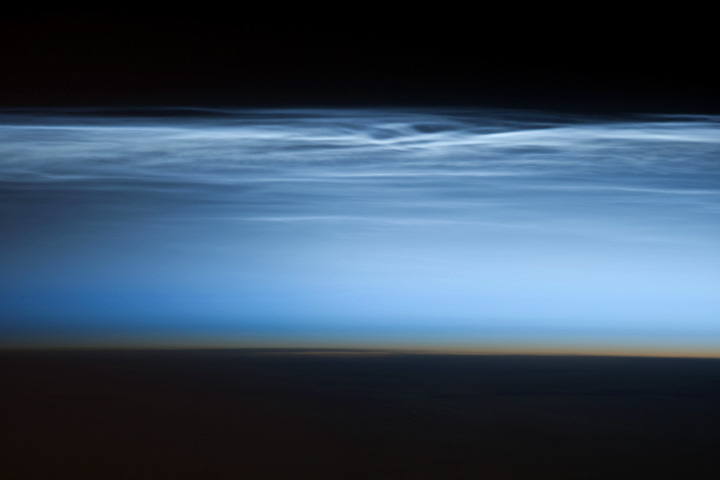
We see noctilucent clouds when most of the sky has grown dark, but the rays from the sun can still reach and reflect off these eerie, ethereal clouds. Indeed, they have an electric-blue appearance. When satellites or astronauts view them from space, they go by the name of polar mesospheric clouds. If you want to see them for yourself, now’s the time to look!

Where to watch for noctilucent clouds
As with the aurora, it helps to be closer to the poles to see this phenomenon. You can keep tabs on noctilucent clouds via SpaceWeather’s RealTime gallery, or on Facebook via the group Noctilucent Clouds Around the World.
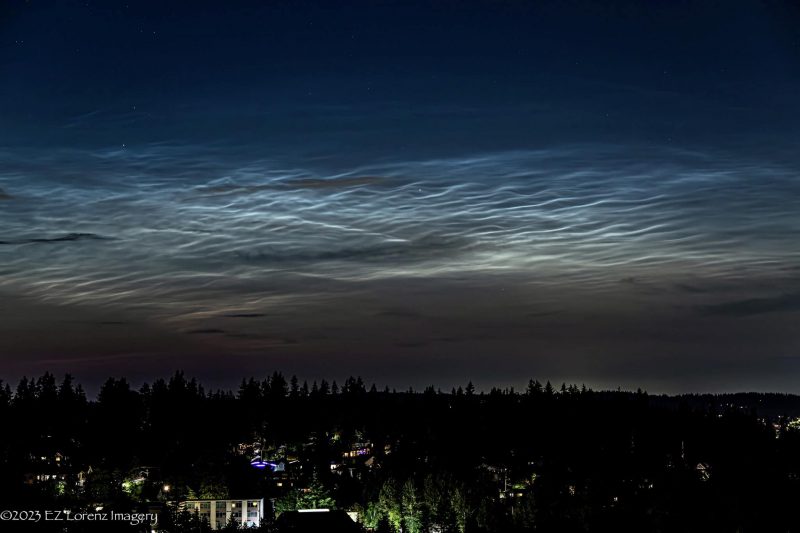

It’s noctilucent cloud season
The season for noctilucent clouds at northerly latitudes is now. People at high latitudes report seeing noctilucent clouds. This happens every year, from about May through August in the Northern Hemisphere, and from November through February in the Southern Hemisphere.
In recent years, northern summertime noctilucent clouds have set records for low-latitude sightings. In 2019, for example, people observed them as far south as Las Vegas (36 degrees north latitude) and Los Angeles (34 degrees north latitude). Usually, though, they’re seen from higher latitudes.

How to see these night-shining clouds
To see noctilucent clouds, you’ll want to have certain conditions in your favor. One factor is when to look. Right about now – June to July – is typically when noctilucent clouds are most widespread.
You’ll also want to be positioned as far north as possible during the Northern Hemisphere’s peak season. Canada and the U.K. are two locations where you’ll have a better chance to spot night-shining clouds. (However, rocket launches can inject particles into the upper atmosphere and make noctilucent clouds visible to areas that aren’t so far north.)
Then, look west about 30 minutes after sunset. The farther north you are, the longer throughout the night you can see them. That’s because the sun doesn’t dip as far below your horizon.
Noctilucent clouds look like electric, luminous tendrils of blue-white light. They are the clouds that glow after other clouds have darkened.
What noctilucent clouds can teach us
Noctilucent clouds are sensitive to atmospheric temperatures. Therefore, they can act as a proxy for information about the wind circulation that causes these temperatures. First of all, they can tell scientists that the circulation exists. They can also tell us something about the strength of the circulation.
Scientists studying these clouds have gotten help from NASA’s Aeronomy of Ice in the Mesosphere (AIM) satellite. This satellite, launched in 2007, has observed noctilucent clouds using several onboard instruments to collect information such as temperature, atmospheric gases, ice crystal size and changes in the clouds. It even accounts for the amount of meteoric space dust that enters the atmosphere. You can find out what they are learning at this AIM page.
Studies have also shown that as the climate warms, noctilucent clouds become more visible.
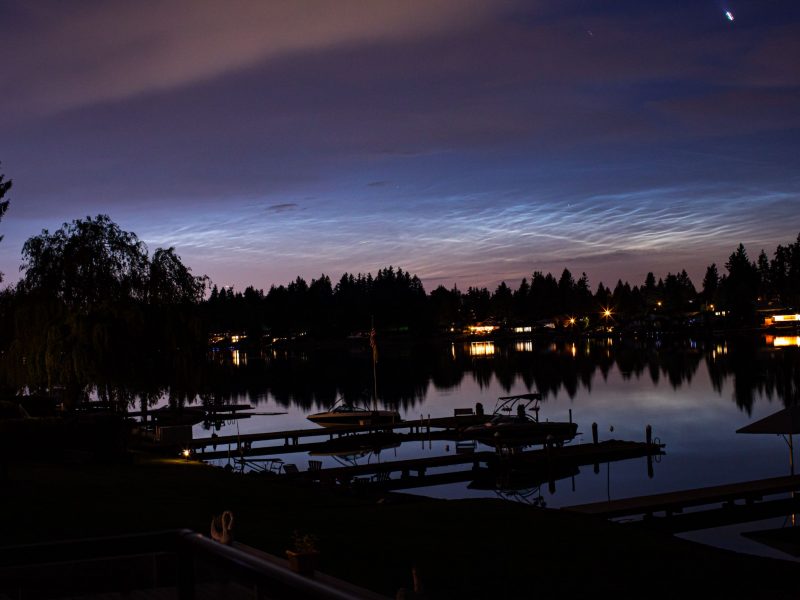
Noctilucent clouds from 2023
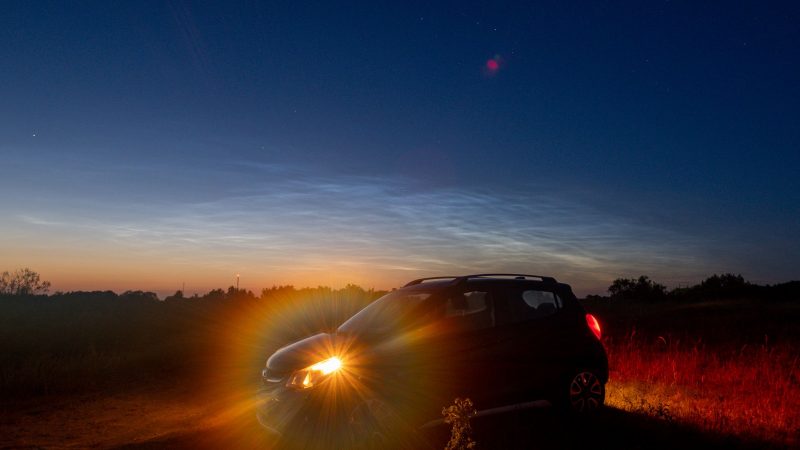



Noctilucent clouds from 2022
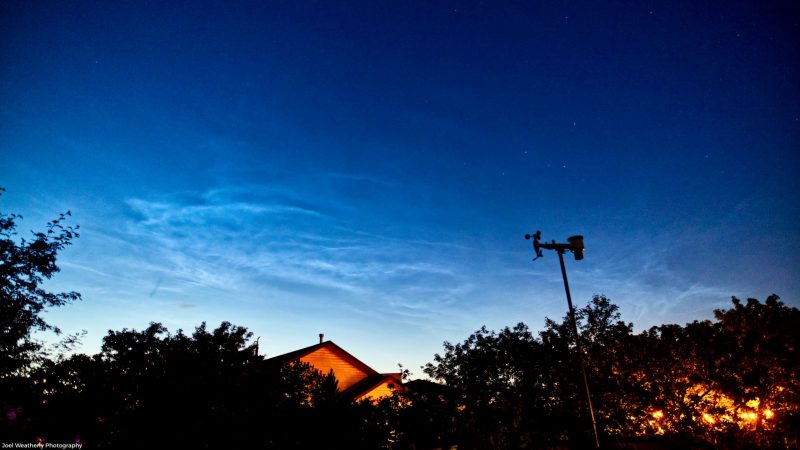
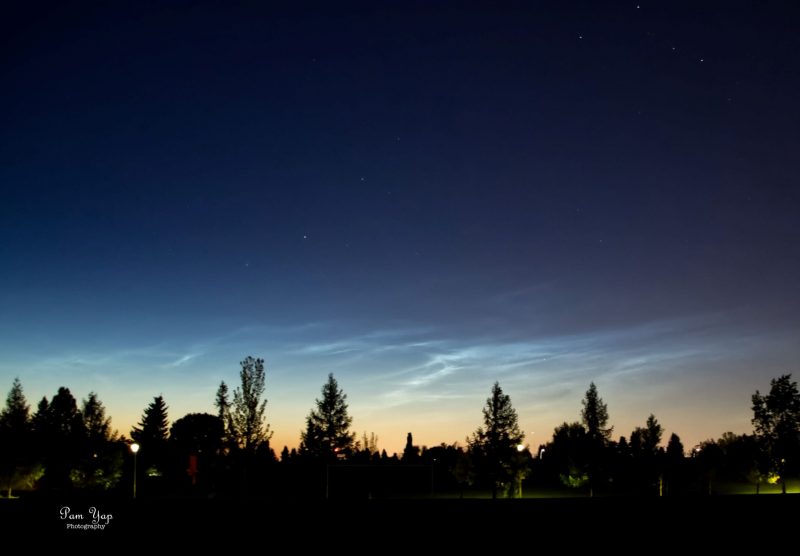



Bottom line: It may be the best noctilucent cloud season in years! Europe has had stunning displays of these night-shining clouds. See a gallery here.











