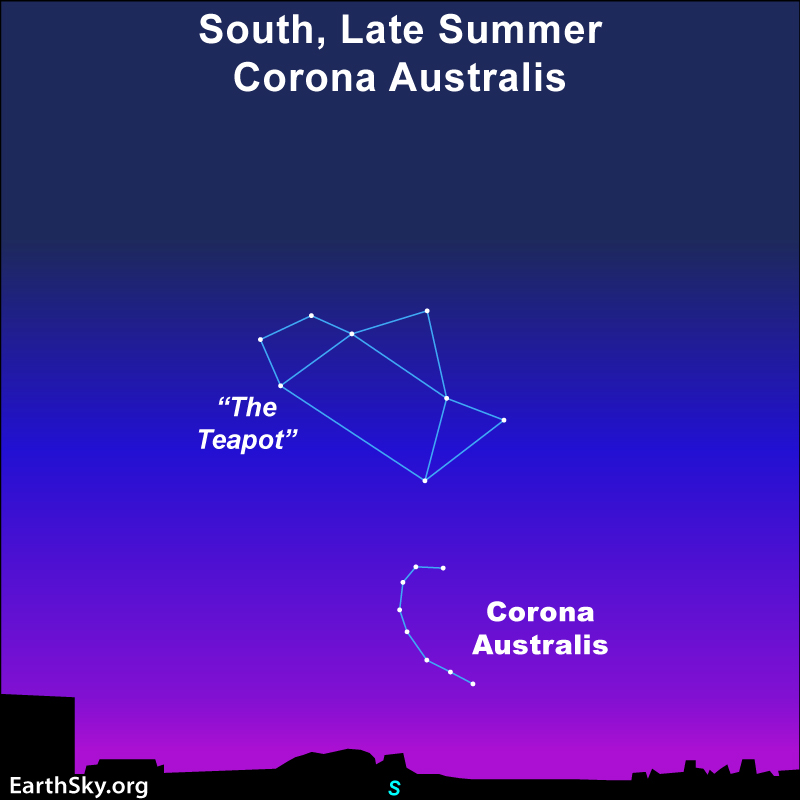
Corona Australis appears as an arc of sparkling stars, one of the few constellations that somewhat resembles the object it’s named for. Ptolemy created Corona Australis in the 2nd century. Ancient Greeks saw this constellation as a wreath, while other civilizations saw a turtle or ostrich nest. It’s quite dim, so you’ll want to be under dark skies to find it. But it’s relatively easy to pick out due to its location just south of major constellations. Corona Australis lies south of the Teapot shape of Sagittarius.
The stars of Corona Australis
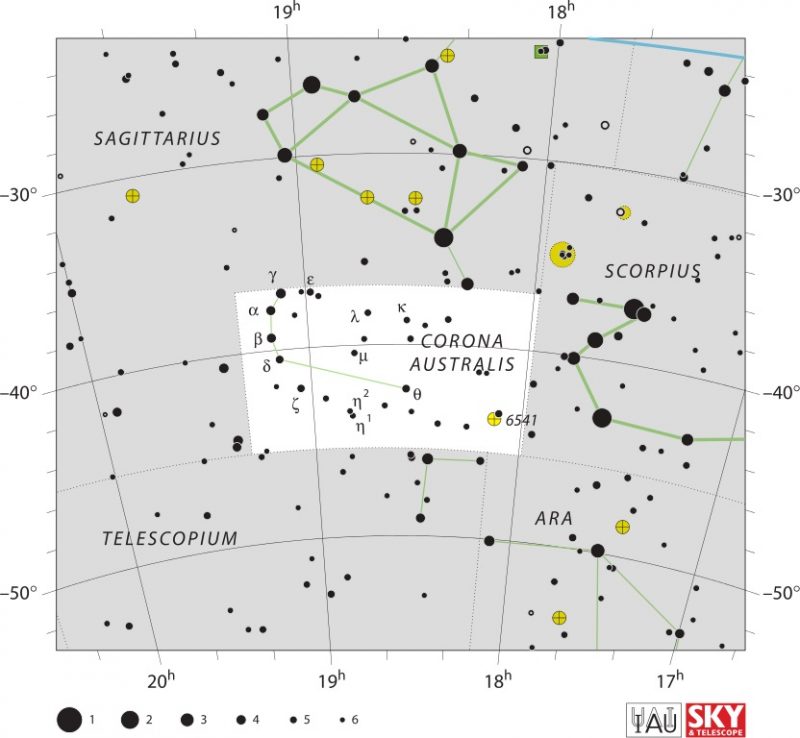
Corona Australis is like its northern cousin, Corona Borealis, in that it forms an arc. But the stars of Corona Australis are so dim that the brightest star is a mere magnitude 4.09. This star, Beta Coronae Australis, lies at the eastern edge of the constellation near the middle of the arc shape. The star lies 508 light-years distant.
The next star to the north in the arc is Alpha Coronae Australis, magnitude 4.11 and 130 light-years distant. Continuing in the same direction along the arc is a magnitude 4.23 star, 58 light-years away: Gamma Coronae Australis. One and a half degrees west of this star is Epsilon Coronae Australis, magnitude 4.83 and 98 light-years away. The last notable star on this side of the arc is just over three degrees away, magnitude 5.11, Lambda Coronae Australis, at 202 light-years distant.
Heading the other direction from Beta is Delta Coronae Australis, a magnitude 4.57 star at a distance of 175 light-years. Next out is Zeta Coronae Australis, magnitude 4.74 and 184 light-years away. At the end of the crown is a double star system, Eta 1 and 2 Coronae Australis, at magnitude 5.46 and 347 light-years away, and magnitude 5.60 and 607 light-years distant, respectively.
Check out this lovely deep-sky image of nebulae in Corona Australis by Hector Rafael Vazquez Rispoli in Buenos Aires, Argentina.
Bottom line: Corona Australis is a dim constellation lying below the Teapot asterism of Sagittarius. Its sparkling, curving shape befits its name.











