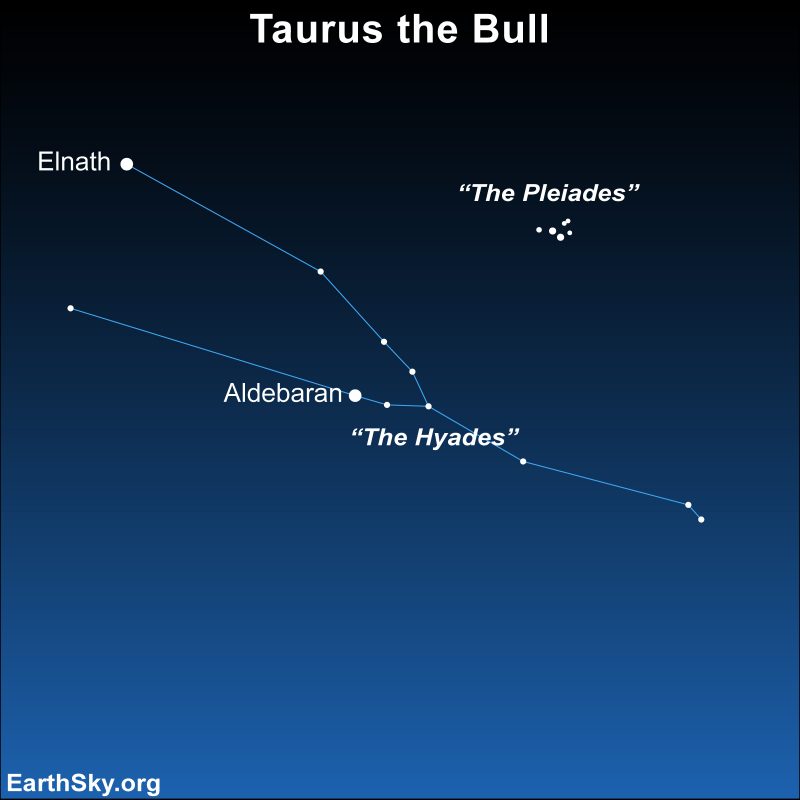
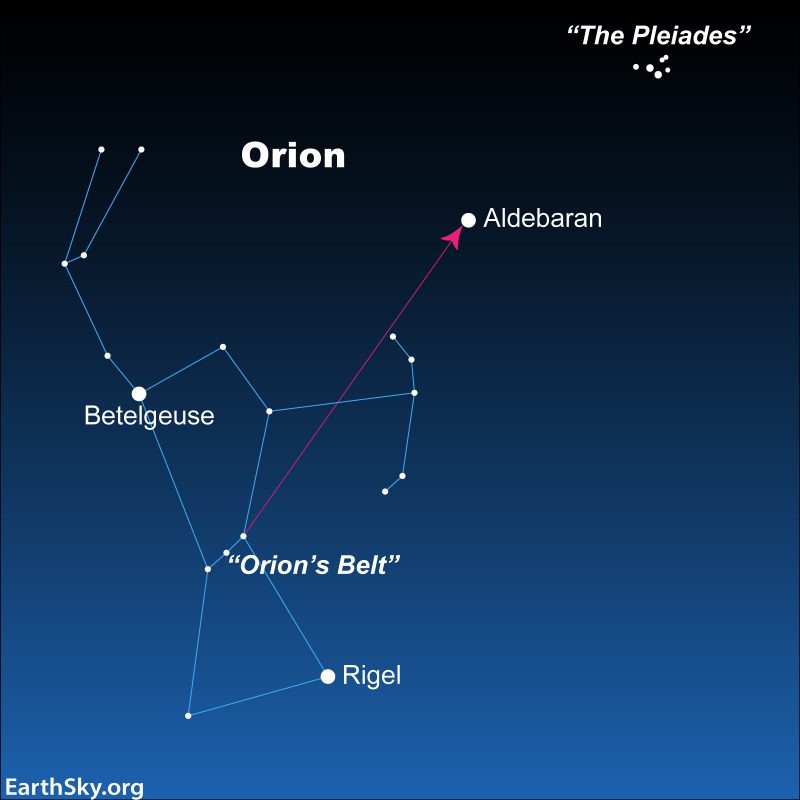
The orange star Aldebaran – the fiery eye of the Bull in the constellation Taurus – is easy to find. It’s part of a V-shaped group of stars – the Hyades – that forms the Bull’s face. You can locate Aldebaran using the famous constellation Orion as a guide. Notice the three stars of Orion’s Belt. Then draw an imaginary line through the Belt to the right. The first bright star you come to will be Aldebaran with its distinctive reddish-orange glow.
The 2024 lunar calendars are here! Best Christmas gifts in the universe! Check ’em out here.
When to spot Aldebaran
Aldebaran is the 14th brightest star, but five of those that outshine it are only barely visible or not visible at all from much of the Northern Hemisphere. Aldebaran is primarily a winter and spring star for us on the northern part of Earth. That’s when this orange star is most easily visible in the evening sky. By early December, it rises shortly after sunset and is visible all night. Three months later it is high to the south at sunset, and sets at around midnight. By early May, it hangs low about the western sunset glow – and before the end of the month, it’s lost altogether. It returns to the predawn sky around late June.
By the way, although it appears among them, Aldebaran is not actually a member of the V-shaped Hyades cluster. It is actually much closer to us in space than the other Hyades stars.
History and mythology of Aldebaran
Artists often depict Aldebaran as the fiery eye of Taurus the Bull. Because it is bright and prominent, ancient Persians honored Aldebaran one of the Four Royal Stars, the other three being Regulus, Antares and Fomalhaut.
The name Aldebaran is from the Arabic for the follower, presumably as a hunter following prey, which was likely the star cluster we call the Pleiades. Some viewed the latter as a flock of birds, perhaps doves. According to Richard Hinckley Allen in his classic book Star Names: Their Lore and Meaning, people once applied the name Aldebaran to the entire Hyades star cluster, a large loose collection of faint stars.
More star lore
In Hindu myth, Aldebaran was a beautiful young woman named Rohini, disguised as an antelope and pursued by her lecherous father, disguised as a deer, Mriga. Several other ancient peoples associated the star with rain. In a Dakota Sioux myth, Aldebaran was a star which had fallen to the Earth and whose killing of a serpent led to the formation of the Mississippi River. Allen notes a number of other alternate names, but precious little mythology is known for Aldebaran separately.
Also, Aldebaran is the name of one of the chariot horses in the movie and book “Ben Hur.”
On a different note, astronomer Jack Eddy has suggested a connection with the Big Horn Medicine Wheel, an ancient circle of stones atop a mountain in Wyoming. Eddy wrote that the ancient Americans may have used this site as a sort of observatory to view the rising of Aldebaran just before the sun in June to predict the June solstice.
Interestingly, in about two million years, the NASA space probe Pioneer 10, now heading out into deep space, will pass Aldebaran.
Science of Aldebaran
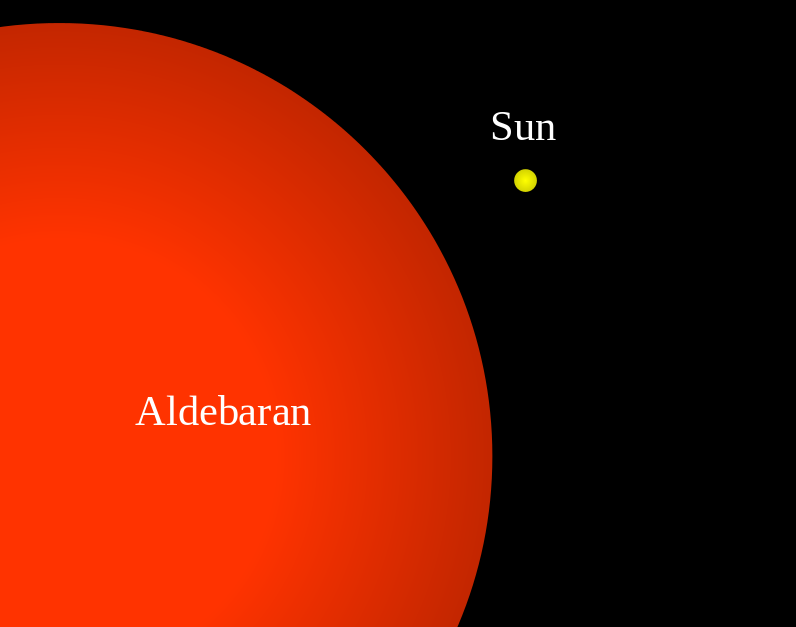
Aldebaran is a huge aging star. The diameter is about 44 times the size of our sun. If Aldebaran replaced our sun, its surface would extend past the orbit of Mercury.
Aldebaran glows with the orangish color of a K5 giant star. In visible light, it is about 153 times brighter than the sun, although its surface temperature is lower, roughly 4,000 K (about 3,700 degrees C or 6,700 degrees F) compared to 5,800 K (about 5,500 C or 10,000 F) for the sun.
Although Aldebaran is associated with the stars of the Hyades, it’s much closer at 65 light-years distant. The Hyades are about 150 light-years away.
Aldebaran is an erratic variable with minor variations too small to see with the eye. Also, five faint stars are visible near Aldebaran, but so far none have been confirmed to be gravitationally bound to Aldebaran.
Aldebaran’s position is RA: 4h 35m 55s, dec: 16°30’35”
Bottom line: Aldebaran is an enormous, orange-colored star that marks one of the eyes of Taurus the Bull. It also marks one point of the V-shape of the Bull’s face.