Using improved methods of analysis of uranium and lead isotopes, the current study of primitive meteorites has enabled researchers to date the formation of two very different types of materials, so-called calcium-aluminum-rich inclusions (or CAI’s for short) and chondrules, found within the same meteorite. By doing so, the chronology and therefore overall understanding of our solar system’s development has been altered. The study has just been published in the renowned scientific journal, Science.

4.567 billion years – this is how far back we must travel to experience our nascent solar system. The researchers at the University of Copenhagen Centre for Star and Planet Formation took a closer look at the first three million years of the solar system’s development by analysing primitive meteorites composed of a blend of our solar system’s very oldest materials. In part, the study confirmed previous analyses demonstrating that CAI’s were formed during a very short period of time. The new discovery is that the so-called chondrules were formed during the first three million years of the solar system’s development as well. This stands in contrast with previous assumptions asserting that chondrules only started forming roughly two million years after CAIs.
Painting a new picture of the Solar System
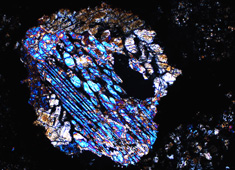
“By using this process to date the formation of these two very different types of materials found in the same meteorite, we are not only able to alter the chronology of our solar system’s historical development, we are able to paint a new picture of our solar system’s development, which is very much like the picture that other researchers have observed in other planetary systems,” says James Connelly of the Centre for Star and Planet Formation.
We aren’t that special…
Showing that chondrules are as old as CAIs addresses a long-standing question of why chondrule formation should be delayed by up to 2 million years after CAIs. The answer – it is not.
“In general, we have shown that we are not quite as unique as we once thought. Our solar system closely resembles other observable planetary systems within our galaxy. In this way, our results serve to corroborate other research results which indicate that earth-like planets are more widespread in the universe than previously believed,” says Professor Martin Bizzarro, head of the Centre for Star and Planet Formation.











