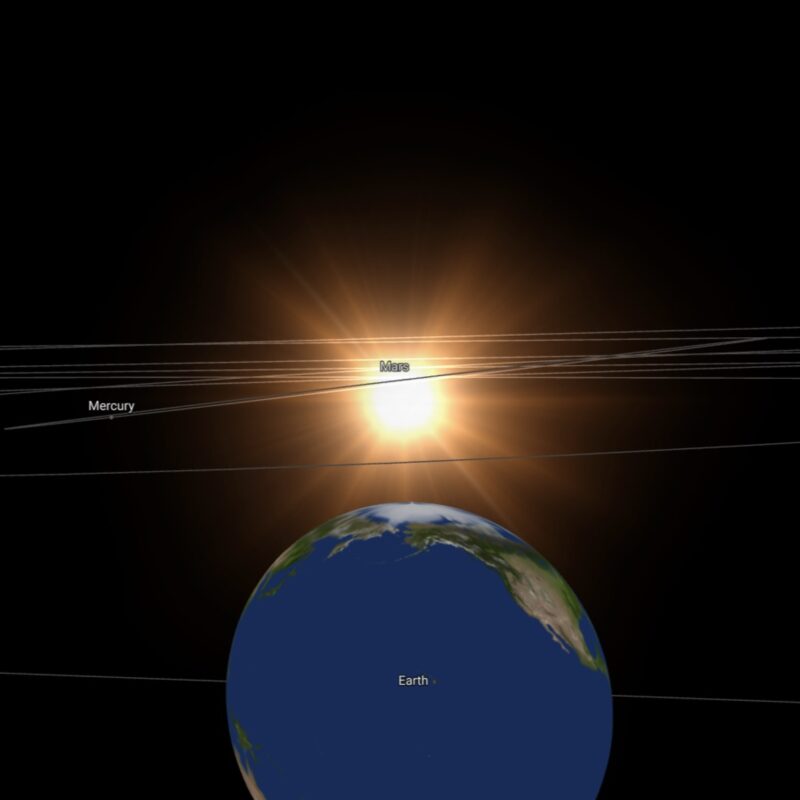
Between now and early December, radio signals used to send commands from Earth to Mars spacecraft – and to receive signals from the spacecraft – can be disturbed by the sun’s corona, its outermost atmosphere. So communications from Earth with spacecraft, landers, rovers and future humans at the red planet are currently limited. Reprinted from the European Space Agency. Edits by EarthSky.
The 2024 lunar calendars are here! Best Christmas gifts in the universe! Check ’em out here.
Mars spacecraft fall silent
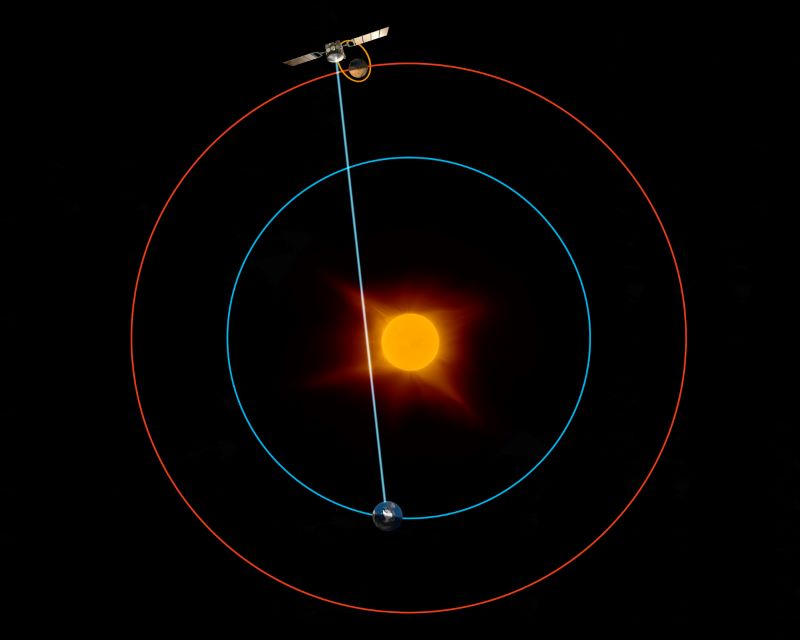
The space between Earth and Mars is usually buzzing with science data, telemetry and commands racing to and from almost a dozen missions at the red planet. But for roughly 1 1/2 days, communication between the planets will fall silent as Mars passes behind the sun on November 18.
Solar conjunction for Mars occurs roughly once every 25 months. During conjunction, Mars is located on the opposite side of the sun from Earth.
Around the time of conjunction, the radio signals used to send commands from Earth to the spacecraft and to receive signals from the spacecraft can be disturbed by the sun’s active atmosphere, the solar corona.
The period of time during which communications are significantly disturbed depends on the size and power of a Mars spacecraft’s communication equipment. But it typically takes place while the angle in the sky between the sun and Mars as seen from Earth is within 3 to 4 degrees.
In 2023, this period lasts from early November to early December.
No earthly instructions for Mars spacecraft
As a result of the disruption, mission controllers can’t reliably send commands to, or receive data from, their spacecraft. Special precautions have to be taken.
For ESA’s Mars Express and ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter (known as MEX and TGO, because we enjoy our acronyms), this means uplinking all the critical instructions the spacecraft would need to operate without any contact from Earth for the entire period. That’s three or four weeks of commands when we normally send up only one week at a time.
Of course, these conjunctions also affect the missions of other space agencies, and this kind of thing isn’t unique to Mars.

Ground stations to full power!
Due to the disturbance from the sun’s atmosphere during conjunction season, we have to reduce the amount of data we exchange with MEX and TGO.
We cut the amount of data that we “uplink” to MEX, for example, down from 2000 bits per second to just 250, and reduce the amount of data that MEX sends down to Earth to as little as 300 bits per second.
We also set our Estrack ground stations to maximum transmission power to make sure our spacecraft hears us loud and clear despite the disturbance, i.e., we use a louder voice but say fewer words.
This limits the kind of information that MEX can send to its operators on Earth to “housekeeping” data – health status and telemetry – and is too low for MEX to send any science data.
Like a diver holding their breath, any data gathered by MEX’s instruments during the conjunction period must be stored in the limited onboard memory until the period is over.
What makes the 2023 conjunction special?
Mars Express arrived at the red planet on December 25, 2003, and is one of Europe’s longest-serving missions. The team celebrated 20 years since launch this summer with the 1st-ever live webcast from another planet.
This will be MEX’s tenth solar conjunction and TGO’s third. However, as the orbits of Mars and Earth have slightly different inclinations, Mars doesn’t usually pass directly behind the sun.
The 2023 conjunction is unusual in that it will be the first time that Mars passes behind the disk of the sun since the two ESA spacecraft arrived.
While Mars is behind the sun, for roughly 1 1/2 days on November 17-18, communication with MEX and TGO won’t just be limited, it’ll be impossible.
These windows of limited or impossible communication between Earth and Mars will pose a challenge for future human settlers, too.


Are you worried?
James Godfrey, Spacecraft Operations Manager for Mars Express. said:
At the beginning of the mission, the team was very cautious about conjunctions. If something goes seriously wrong during the conjunction period, it could be difficult to recover the spacecraft until it’s over.
We used to suspend all science operations. But, over the years, we’ve only ever experienced minor disruptions.
In 2019, we discovered that we can continue using some of MEX’s instruments in a limited way, as long as all commands are uploaded before the season begins, and all science data are stored on board until the season ends.
Originally, planning for conjunctions was a very manual process. But over the years, it’s become largely routine.
Peter Schmitz, Spacecraft Operations Manager for Trace Gas Orbiter, added:
With its larger communications antenna and data storage capacity, TGO is able to continue with its data relay activities for Mars surface assets throughout the conjunction period – even when Mars is directly behind the sun – and prepare to downlink all of the stored data to Earth when it is once again safe to do so.
Bottom line: Solar conjunction for Mars happened yesterday, November 18, 2023. That’s when Mars was most directly behind the sun for this 25-month period. In 2023, the season of Mars’ conjunction takes place between November 5 and December. During this period, data exchange between Mars spacecraft and Earth is limited.











