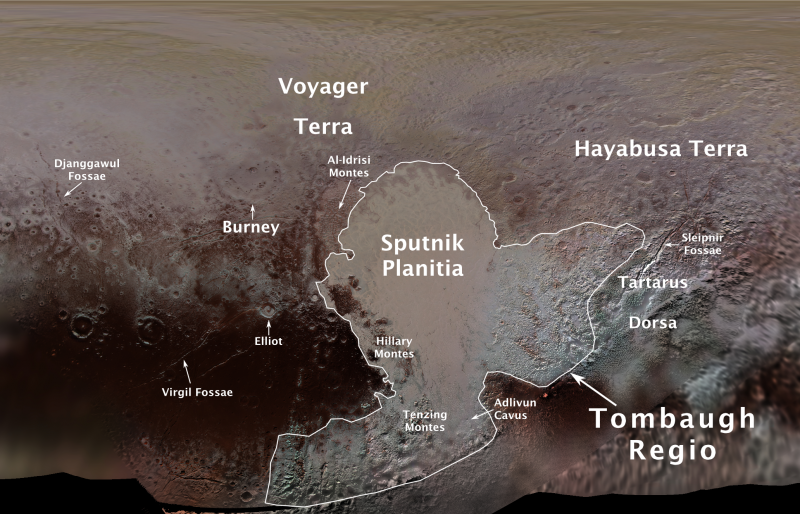
Pluto’s “heart” now bears the name of pioneering American astronomer Clyde Tombaugh, who discovered Pluto in 1930. And a crater on Pluto is now officially named after Venetia Burney, the British schoolgirl who in 1930 suggested the name Pluto, for the newly-discovered world.
These are two of 14 official Pluto feature names approved by the International Astronomical Union (IAU), the internationally recognized authority for naming celestial bodies and their surface features.
These and other names were proposed by NASA’s New Horizons team following the first reconnaissance of Pluto and its moons by the New Horizons spacecraft in 2015. The team gathered many ideas during the “Our Pluto” online naming campaign in 2015.
The approved Pluto surface feature names are listed below, from a NASA statement. The names pay homage to the underworld mythology, pioneering space missions, historic pioneers who crossed new horizons in exploration, and scientists and engineers associated with Pluto and the Kuiper Belt.
– Tombaugh Regio honors Clyde Tombaugh (1906–1997), the U.S. astronomer who discovered Pluto in 1930 from Lowell Observatory in Arizona.
– Burney crater honors Venetia Burney (1918-2009), who as an 11-year-old schoolgirl suggested the name “Pluto” for Clyde Tombaugh’s newly discovered planet. Later in life she taught mathematics and economics.
– Sputnik Planitia is a large plain named for Sputnik 1, the first space satellite, launched by the Soviet Union in 1957.
– Tenzing Montes and Hillary Montes are mountain ranges honoring Tenzing Norgay (1914–1986) and Sir Edmund Hillary (1919–2008), the Indian/Nepali Sherpa and New Zealand mountaineer were the first to reach the summit of Mount Everest and return safely.
– Al-Idrisi Montes honors Ash-Sharif al-Idrisi (1100–1165/66), a noted Arab mapmaker and geographer whose landmark work of medieval geography is sometimes translated as “The Pleasure of Him Who Longs to Cross the Horizons.”
– Djanggawul Fossae defines a network of long, narrow depressions named for the Djanggawuls, three ancestral beings in indigenous Australian mythology who traveled between the island of the dead and Australia, creating the landscape and filling it with vegetation.
– Sleipnir Fossa is named for the powerful, eight-legged horse of Norse mythology that carried the god Odin into the underworld.
– Virgil Fossae honors Virgil, one of the greatest Roman poets and Dante’s fictional guide through hell and purgatory in the Divine Comedy.
– Adlivun Cavus is a deep depression named for Adlivun, the underworld in Inuit mythology.
– Hayabusa Terra is a large land mass saluting the Japanese spacecraft and mission (2003-2010) that performed the first asteroid sample return.
– Voyager Terra honors the pair of NASA spacecraft, launched in 1977, that performed the first “grand tour” of all four giant planets. The Voyager spacecraft are now probing the boundary between the Sun and interstellar space.
– Tartarus Dorsa is a ridge named for Tartarus, the deepest, darkest pit of the underworld in Greek mythology.
– Elliot crater recognizes James Elliot (1943-2011), an MIT researcher who pioneered the use of stellar occultations to study the solar system – leading to discoveries such as the rings of Uranus and the first detection of Pluto’s thin atmosphere.
Bottom line: the International Astronomical Union (IAU) gave official names to 14 geological features on Pluto.











