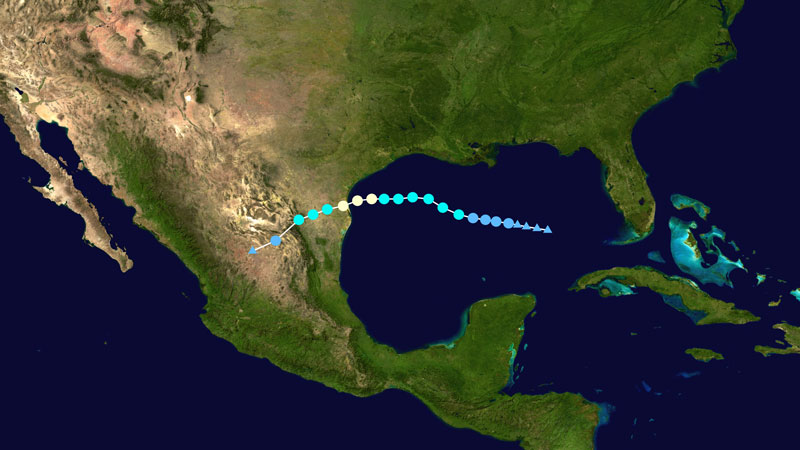
Thanks to July’s Hurricane Hanna, the Gulf of Mexico’s dead zone is much smaller this summer than usual. Researchers say the storm stirred up the area of low-oxygen water. This week’s Tropical Storm Marco and Hurricane Laura – currently causing havoc in the Gulf – are likely further disrupting the Gulf’s 2020 dead zone.
Hurricanes are largely thankless affairs with damaging winds and heavy rains that can cause extensive flooding along coastal regions. But for some marine life in the Gulf of Mexico, a hurricane may just mean they get a bit of a reprieve from the dead zone, an area of stagnant, low-oxygen water that forms every summer off the coast. During a July 2020 research cruise, scientists found that Hurricane Hanna had disrupted the formation of the dead zone, which was much smaller than usual for that time of year.
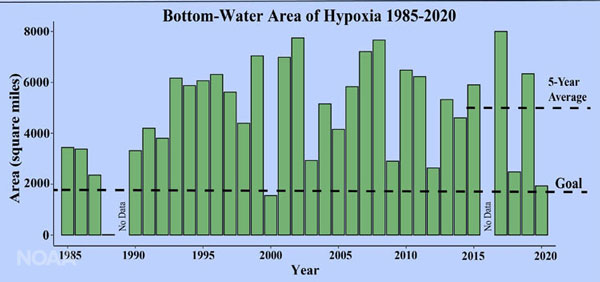
Scientists have been tracking the Gulf of Mexico dead zone since 1985. This large area of low-oxygen water develops every summer in response to nutrient inputs from the Mississippi River. These nutrients, along with warm water and sunlight, stimulate the growth of algae, which eventually die off and are decomposed by bacteria. During the process, the bacteria use up most of the dissolved oxygen in the water, and this creates conditions inhospitable to marine life. The dead zone eventually disappears when cooler weather arrives in the fall.
To help maintain a healthy coastal region and robust fisheries in the Gulf of Mexico, efforts are underway to reduce nutrient runoff into the Mississippi River basin from agricultural lands and other sources. Tracking of the annual size of the dead zone is an important way to monitor the effectiveness of these conservation efforts. Over the past five years, the size of the dead zone has averaged 5,408 square miles (14,007 square kilometers), which is similar to the area of Puerto Rico. This average size is nearly three times the goal of the Mississippi River/Gulf of Mexico Hypoxia Task Force, which aims to reduce the running five-year average size of the dead zone to no more than 1,930 square miles (approximately 5,000 square kilometers).
This year’s dead zone measured only 2,116 square miles (5,480 square kilometers), which is much smaller than the typical size. Overall, the dead zone in 2020 ranked as the third smallest in the 34-year historical record. According to the scientists responsible for monitoring the dead zone, Hurricane Hanna passed through the area just prior to the measurements and stirred up the waters, which greatly reduced the size of the dead zone. Because nutrient runoff into the Mississippi River basin remains high, the small size of the dead zone in 2020 can be attributed to the weather and not substantial reductions in nutrient loading to the Gulf.
Nancy Rabalais, a Louisiana State University professor and chief scientist for the Gulf of Mexico dead zone monitoring efforts, commented on the new findings in a statement. She said:
The passage of Tropical Storm/Hurricane Hanna across the central Gulf generated 5- to 6- and occasional 8-foot waves along the inner shelf, and mixed the water column down to about 15 to 20 meters [50 to 65 feet]. The consistent winds from the south generated downwelling favorable conditions, and the remaining low oxygen was farther offshore, in deeper water than normally. Vertically uniform temperature, salinity and dissolved oxygen data across the broad area mapped is not the norm for a July shelf-wide hypoxia cruise.
Hurricane Hanna was the first such storm of the 2020 hurricane season in the Atlantic basin. It became a tropical storm on July 24 within the Gulf of Mexico and intensified into a hurricane on July 25. The hurricane made landfall in Texas later that day as a category 1 hurricane. This year is expected to be a very active hurricane season. As of August 25, 2020, two tropical disturbances, one a hurricane, are now traversing the Gulf. These storms also have the potential to disrupt the dead zone.
In addition to the high winds and waves at the beginning of the research cruise, the crew also faced unique challenges stemming from the Covid-19 pandemic. In particular, advanced SARS-CoV-2 tests were conducted on crew members prior to boarding the vessel and there was a reduced crew size this year.

Steven Thur, director of NOAA’s National Centers for Coastal Ocean Science, said:
The data collected from this annual, long-term research program is critical to our understanding of a wide range of Gulf issues including hypoxia. Not only is measuring the size of the Gulf of Mexico dead zone vital to informing the best strategy to reduce its size, but also to reduce its impacts on the sustainability and productivity of our coastal resources and economy.
Bottom line: The annual size of the Gulf of Mexico dead zone was much smaller than usual in 2020 because the area of low-oxygen water was stirred up by Hurricane Hanna.











